| Sv translation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
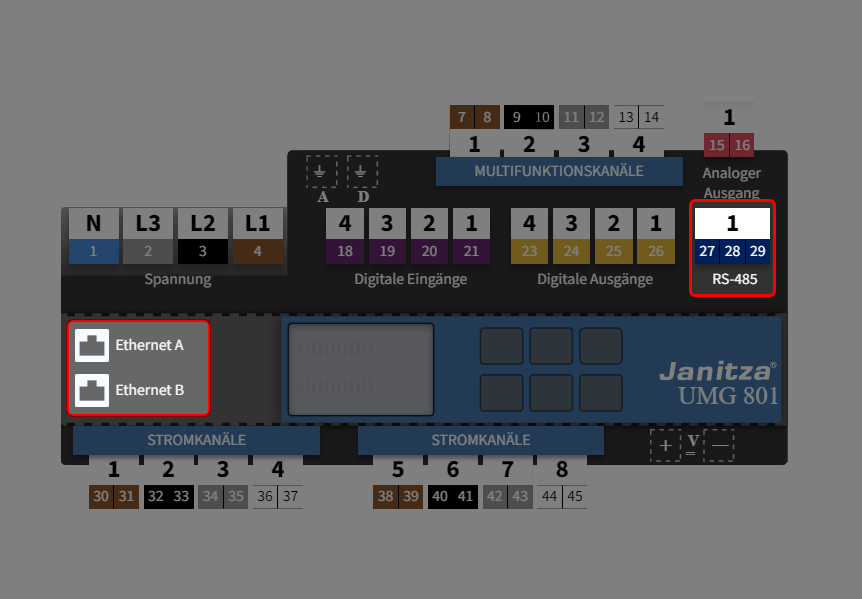
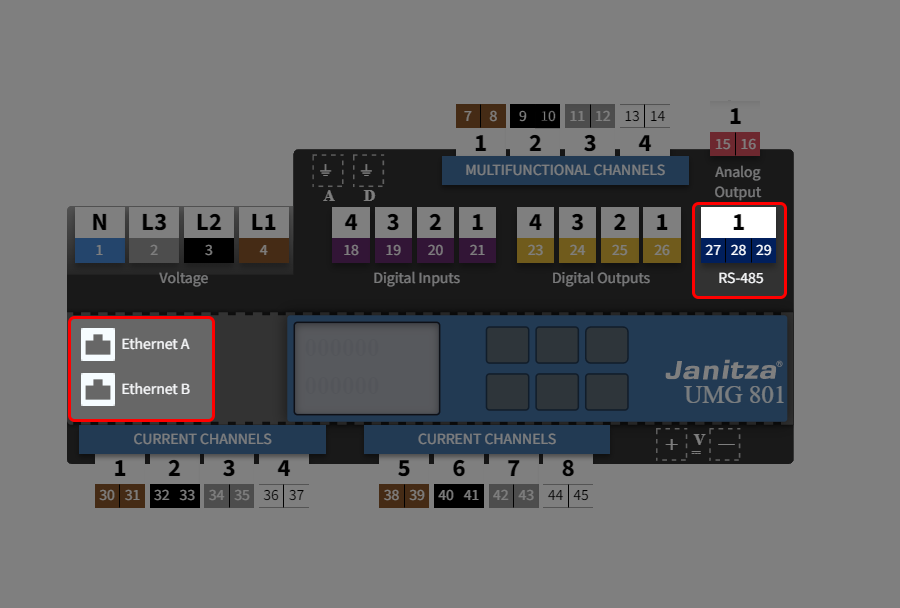
Welche Schnittstellen kann ich mit dem Gerät verwenden? Ethernet (Modbus/TCP) und RS485 (Modbus RTU)
|
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Sachschaden durch falsche Netzwerkeinstellungen!
|
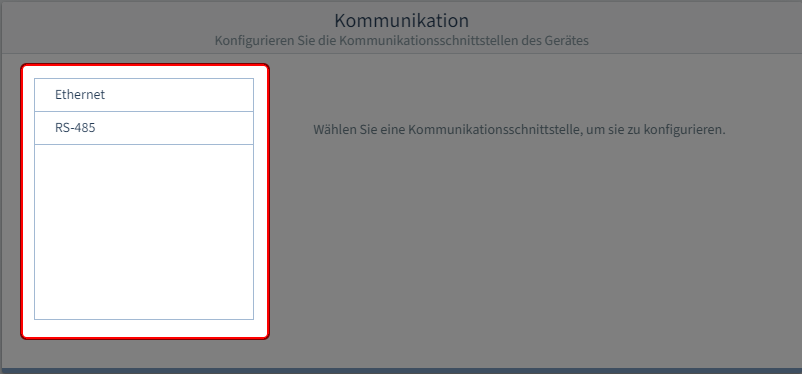
Wie konfiguriere ich die Schnittstellen?
SCHRITT 1 - 2
Schnittstelle auswählen
SCHRITT 2 - 2 / OPTION 1
Ethernet (Modbus/TCP)
SCHRITT 2 - 2 / OPTION 2
RS485 (Modbus RTU)
(Zum Vergrößern auf das Vorschaubild klicken)
(Zum Vergrößern auf das Vorschaubild klicken)
(Zum Vergrößern auf das Vorschaubild klicken)
Wählen Sie die Schnittstelle aus.
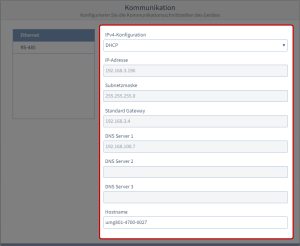
- IPv4-Konfiguration
Wählen Sie die Art der Adressvergabe der Ethernet-Verbindung (TCP/IP):
DHCP (Standardeinstellung)
Das Gerät erhält beim Start automatisch IP-Adresse, Netzmaske und Gateway vom DHCP-Server.
Bei dieser Auswahl ist nur noch der Hostname einstellbar.
Alle weiteren Parameter sind vorgegeben.
Statische IP-Adresse
Parametrieren Sie die Kommunikations-Schnittstelle nach eigenen Anforderungen. Verwenden Sie diesen Modus für einfache Netzwerke ohne DHCP-Server.
- IP-Adresse
Einstellung nur erforderlich, wenn zur Adressvergabe Feste IP-Adresse gewählt wurde. - Subnetzmaske
Einstellung nur erforderlich, wenn zur Adressvergabe Feste IP-Adresse gewählt wurde.
- Standard Gateway
Einstellung nur erforderlich, wenn zur Adressvergabe Feste IP-Adresse gewählt wurde.
- DNS Server
Einstellung nur erforderlich, wenn zur Adressvergabe Feste IP-Adresse gewählt wurde.
- Hostname
Vergeben Sie einen Hostname für das System.
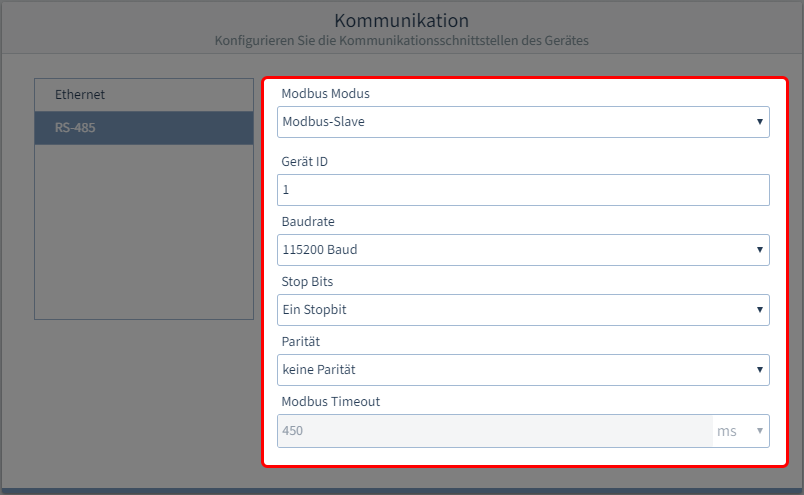
- Modbus Modus
Modbus-Server (Slave)
Das Gerät ist in einer Busstruktur als Server angelegt.
Modbus-Client (Gateway)
Das Gerät ist der Client eine Busstruktur.
- Geräte ID
Wählen Sie eine Geräteadresse, mit der das Gerät in der Bus-Struktur angesprochen
wird. Jede Geräteadresse existiert in einer Bus-Struktur einmal.Einstellbereich: 1.. 247 (gemäß Modbus-Standard)
1 (Standardeinstellung)
- Baudrate
Wählen Sie für alle Geräte in der Busstruktur eine einheitliche Baudrate.
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 Bd (Standardeinstellung)
- Stoppbit
Wählen Sie für alle Geräte in der Busstruktur einen einheitlichen Datenrahmen.
Ein Stoppbit (Standardeinstellung)
Zwei Stoppbits
- Parität
Wählen Sie für alle Geräte in der Busstruktur einen einheitlichen Datenrahmen.
keine
gerade
ungerade (Standardeinstellung)
- Modbus Timeout
Modus Modbus-Slave
Nicht einstellbar.
Modus Modbus-Gateway
1.. 450 ms
Bei Auswahl eines Timeouts außerhalb dieses Zeitbereichs, kommt es zu einer Fehlermeldung.
| Sv translation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
Which interfaces can I use with the device? Ethernet (Modbus/TCP) and RS-485 (Modbus RTU)
|
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Material damage due to incorrect network settings!
|
How do I configure the interfaces?
STEP 1 - 2
Select interface
STEP 2 - 2 / OPTION 1
Ethernet (Modbus/TCP)
STEP 2 - 2 / OPTION 2
RS-485 (Modbus RTU)
(Click on the thumbnail to enlarge it)
(Click on the thumbnail to enlarge it)
(Click on the thumbnail to enlarge it)
Select the interface.
- IPv4 configuration
Select the type of address assignment for the Ethernet connection (TCP/IP):
DHCP (default setting)
On start-up, the device is automatically given an IP address, netmask and gateway by the DHCP server.
With this selection, only the hostname can be set.
All other parameters are preset.
Static IP address
Configure the communication interface parameters according to your own requirements. Use this mode for simple networks with no DHCP server.
- IP address
Setting only required if Fixed IP Address was selected for the address assignment. - Subnet mask
Setting only required if Fixed IP Address was selected for the address assignment.
- Standard gateway
Setting only required if Fixed IP Address was selected for the address assignment.
- DNS server
Setting only required if Fixed IP Address was selected for the address assignment.
- Hostname
Assign a hostname for the system.
- Modbus mode
Modbus server (slave)
The device is created as a server in a bus structure.
Modbus client (gateway)
The device is the client of a bus structure.
- Device ID
Select a device address with which the device can be addressed in the bus structure.
Each device address exists once in a bus structure!Setting range: 1.. 247 (according to Modbus standard)
1 (default setting)
- Baud rate
Select a uniform baud rate for all devices in the bus structure!
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 Bd (default setting)
- Stop bit
Select a uniform data frame for all devices in the bus structure.
One stop bit (default setting)
Two stop bits
- Parity
Select a uniform data frame for all devices in the bus structure.
none
even
odd (default setting)
- Modbus timeout
Modbus slave mode
Not configurable.
Modbus gateway mode
1 ... 450 ms
If you select a timeout outside of this time range, there will be an error message.
| Sv translation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
¿Qué interfaces puedo utilizar con el dispositivo? Ethernet (Modbus/TCP) y RS485 (Modbus RTU)
|
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
¡Daños materiales por unos ajustes de red incorrectos!
|
¿Cómo configuro las interfaces?
PASO 1 - 2
Seleccionar la interfaz
PASO 2 - 2 / OPCIÓN 1
Ethernet (Modbus/TCP)
PASO 2 - 2 / OPCIÓN 2
RS485 (Modbus RTU)
(para ampliar, hacer clic en la imagen de vista previa)
(para ampliar, hacer clic en la imagen de vista previa)
(para ampliar, hacer clic en la imagen de vista previa)
Seleccione la interfaz.
- Configuración IPv4
Seleccione el tipo de asignación de dirección de la conexión Ethernet (TCP/IP):
DHCP (ajuste predeterminado)
Durante el inicio, el dispositivo recibe del servidor DHCP automáticamente la dirección IP, la máscara de red y la pasarela.
Con esta selección solo puede ajustarse el nombre del host.
Todos los demás parámetros están preestablecidos.
Dirección IP estática
Parametrice la interfaz de comunicación de acuerdo con sus propias exigencias. Utilice este modo para redes sencillas sin servidor DHCP.
- Dirección IP
Este ajuste solo es necesario si se seleccionó “Dirección IP fija” para la asignación de dirección. - Máscara de subred
Este ajuste solo es necesario si se seleccionó “Dirección IP fija” para la asignación de dirección.
- Pasarela estándar
Este ajuste solo es necesario si se seleccionó “Dirección IP fija” para la asignación de dirección.
- Servidor DNS
Este ajuste solo es necesario si se seleccionó “Dirección IP fija” para la asignación de dirección.
- Nombre del host
Asigne un nombre de host para el sistema.
- Modo Modbus
Servidor Modbus (esclavo)
El dispositivo está creado como esclavo en una estructura de bus.
Cliente Modbus (pasarela)
El dispositivo es el cliente en una estructura de bus.
- ID de dispositivo
Seleccione una dirección de dispositivo con la que se accede al mismo en la estructura de bus.
Cada dirección de dispositivo existe una sola vez en una estructura de bus.Rango de ajuste: 1.. 247 (según estándar Modbus)
1 (ajuste predeterminado)
- Velocidad en baudios
¡Seleccione una velocidad en baudios uniforme para todos los dispositivos en la estructura de bus!
9600, 19.200, 38.400, 57.600, 115.200 Bd (ajuste predeterminado)
- Bit de parada
Seleccione una trama de datos uniforme para todos los dispositivos en la estructura de bus.
Un bit de parada (ajuste predeterminado)
Dos bits de parada
- Paridad
Seleccione una trama de datos uniforme para todos los dispositivos en la estructura de bus.
sin
par
impar (ajuste predeterminado)
- Modbus Timeout
Modo esclavo Modbus
No ajustable.
Modo pasarela Modbus
1 ... 450 ms
Si se selecciona un timeout fuera de este rango de tiempo se produce un mensaje de fallo.
| Sv translation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
Quali interfacce posso utilizzare con il dispositivo? Ethernet (Modbus/TCP) e RS485 (Modbus RTU)
|
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Danni materiali a causa delle impostazioni di rete errate!
|
Come si configurano le interfacce?
PASSAGGIO 1 - 2
Selezionare l’interfaccia
PASSAGGIO 2 - 2 / OPZIONE 1
Ethernet (Modbus/TCP)
PASSAGGIO 2 - 2 / OPZIONE 2
RS-485 (Modbus RTU)
(Cliccare sull’immagine di anteprima per ingrandirla)
(Cliccare sull’immagine di anteprima per ingrandirla)
(Cliccare sull’immagine di anteprima per ingrandirla)
Selezionare l’interfaccia.
- Configurazione IPv4
Selezionare il tipo di assegnazione dell’indirizzo per la connessione Ethernet (TCP/IP):
DHCP (impostazione predefinita)
All’avvio, il dispositivo riceve automaticamente l’indirizzo IP, la netmask e il gateway dal server DHCP.
Con questa selezione è possibile impostare solo il nome dell’host.
Tutti gli altri parametri sono predefiniti.
Indirizzo IP statico
Parametrizzare l’interfaccia di comunicazione in base alle proprie esigenze. Utilizzare questa modalità per reti semplici senza server DHCP.
- IP Address (indirizzo IP)
Impostazione necessaria solo se per l’assegnazione dell’indirizzo è stato selezionato l’indirizzo IP fisso. - Subnet mask
Impostazione necessaria solo se per l’assegnazione dell’indirizzo è stato selezionato l’indirizzo IP fisso.
- Gateway Standard
Impostazione necessaria solo se per l’assegnazione dell’indirizzo è stato selezionato l’indirizzo IP fisso.
- Server DNS
Impostazione necessaria solo se per l’assegnazione dell’indirizzo è stato selezionato l’indirizzo IP fisso.
- Nome host
Assegnare un nome host per il sistema.
- Modalità Modbus
Server Modbus (Slave)
Il dispositivo viene creato come server in una struttura a bus.
Modbus Client (Gateway)
Il dispositivo è il client di una struttura bus.
- ID dispositivo
Selezionare un indirizzo di dispositivo con cui il dispositivo viene indirizzato nella struttura
bus. Ogni indirizzo dispositivo è presente una sola volta in una struttura bus!Campo di regolazione: 1.. 247 (secondo lo standard Modbus)
1 (impostazioni predefinite)
- Velocità di trasmissione
Selezionare la stessa velocità di trasmissione per tutti i dispositivi in una struttura bus.
9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200 Bd (Impostazione predefinita)
- Bit di stop
Selezionare lo stesso frame di dati per tutti i dispositivi in una struttura bus.
Un bit di stop (impostazione predefinita)
Due bit di stop
- Parità
Selezionare lo stesso frame di dati per tutti i dispositivi in una struttura bus.
nessuna
pari
dispari (Impostazione predefinita)
- Timeout del Modbus
Modalità Modbus-Slave
Non impostabile.
Modalità Gateway Modbus
1.. 450 ms
Se si seleziona un timeout al di fuori di questo intervallo, viene visualizzato un messaggio di errore.