Diagrama Sankey
Diagrama Sankey
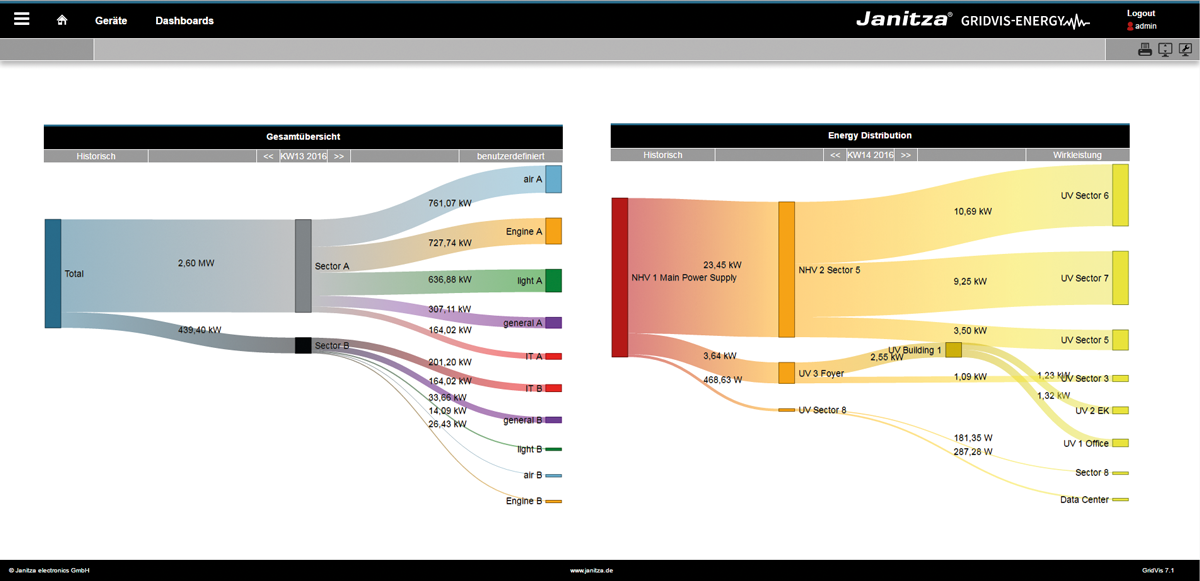
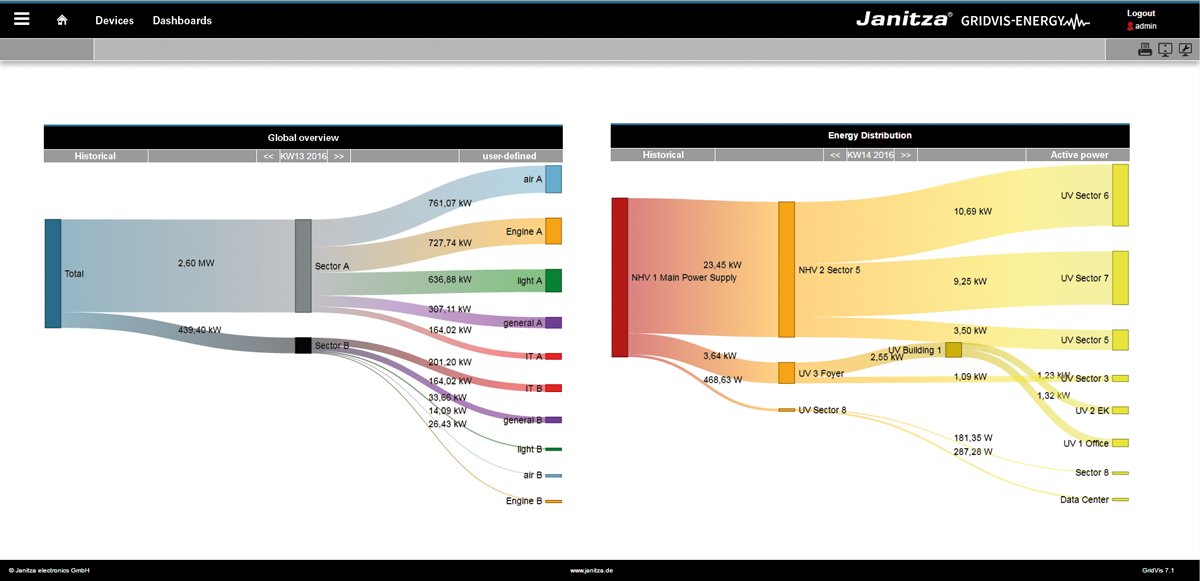
Para los análisis del flujo de la energía se requieren los correspondientes valores de consumo energético, para cuyo análisis se procesan en diagramas informativos sobre el flujo de la energía (diagramas Sankey). Con un diagrama Sankey se obtiene una representación gráfica clara y sintetizada de sus consumos energéticos y otros valores de medición.
Con la función Sankey, compuesta por tres paneles (administrador de Sankey, configurador de Sankey y widget de Sankey), pueden crearse diagramas Sankey adaptados a su empresa de una manera fácil, intuitiva y sin requerir conocimientos de programación; asimismo, dichos diagramas pueden integrarse como widget en cualquier panel para realizar análisis y evaluaciones del flujo de la energía.
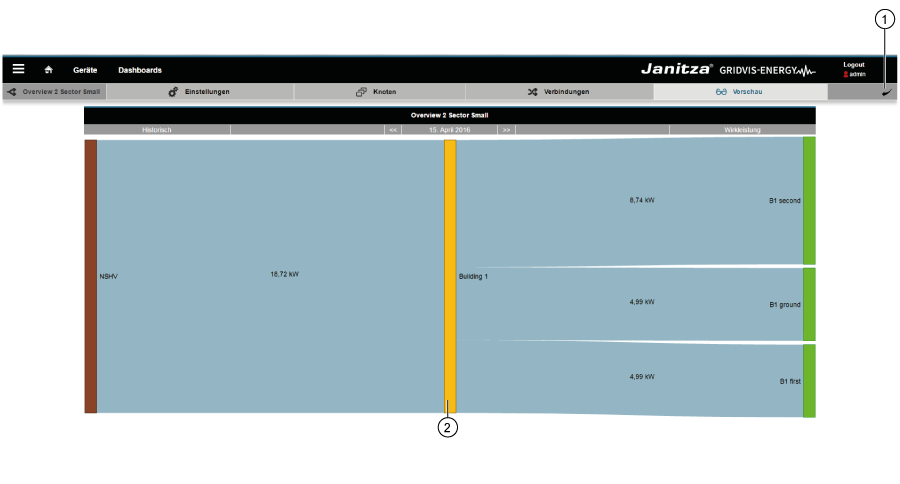
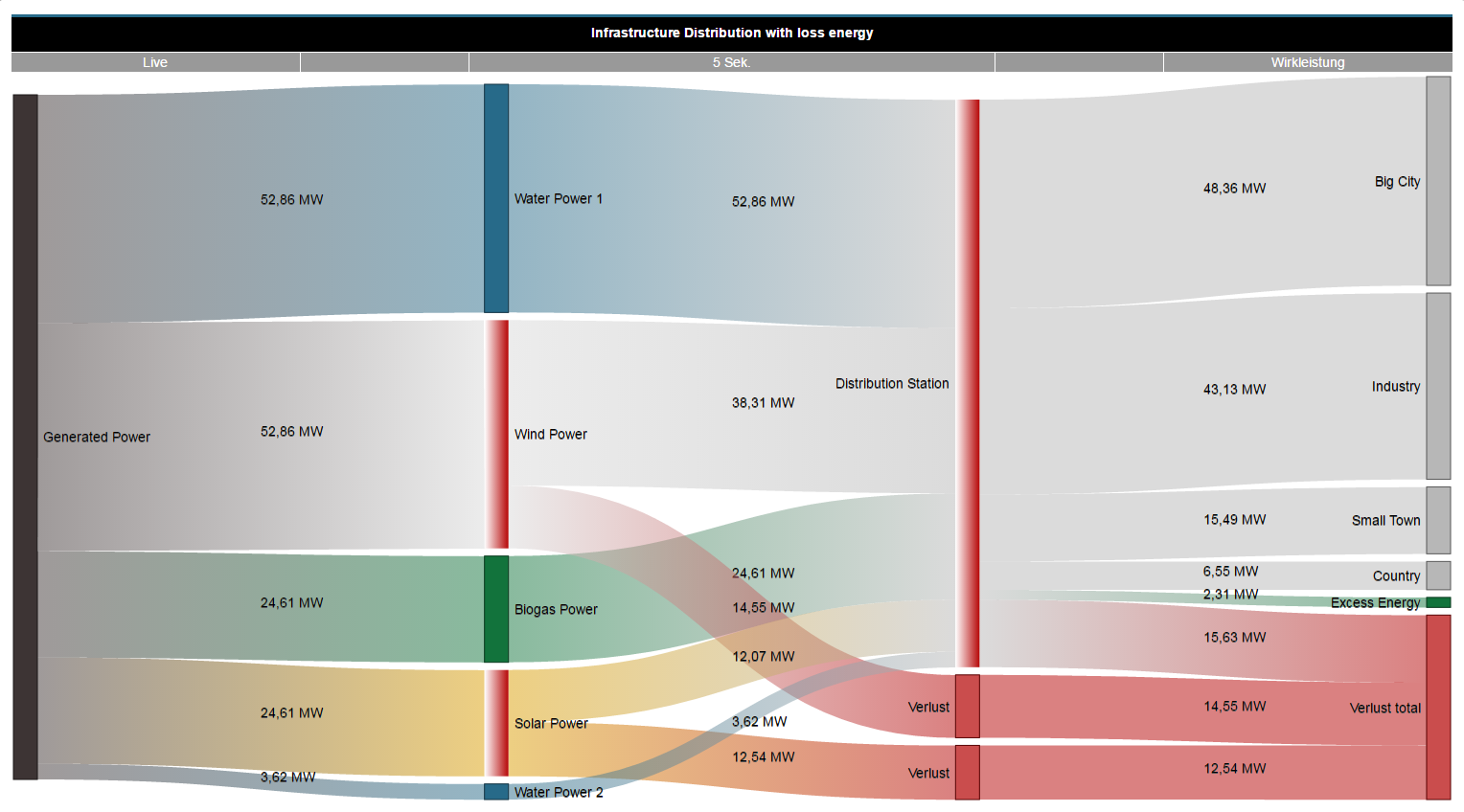
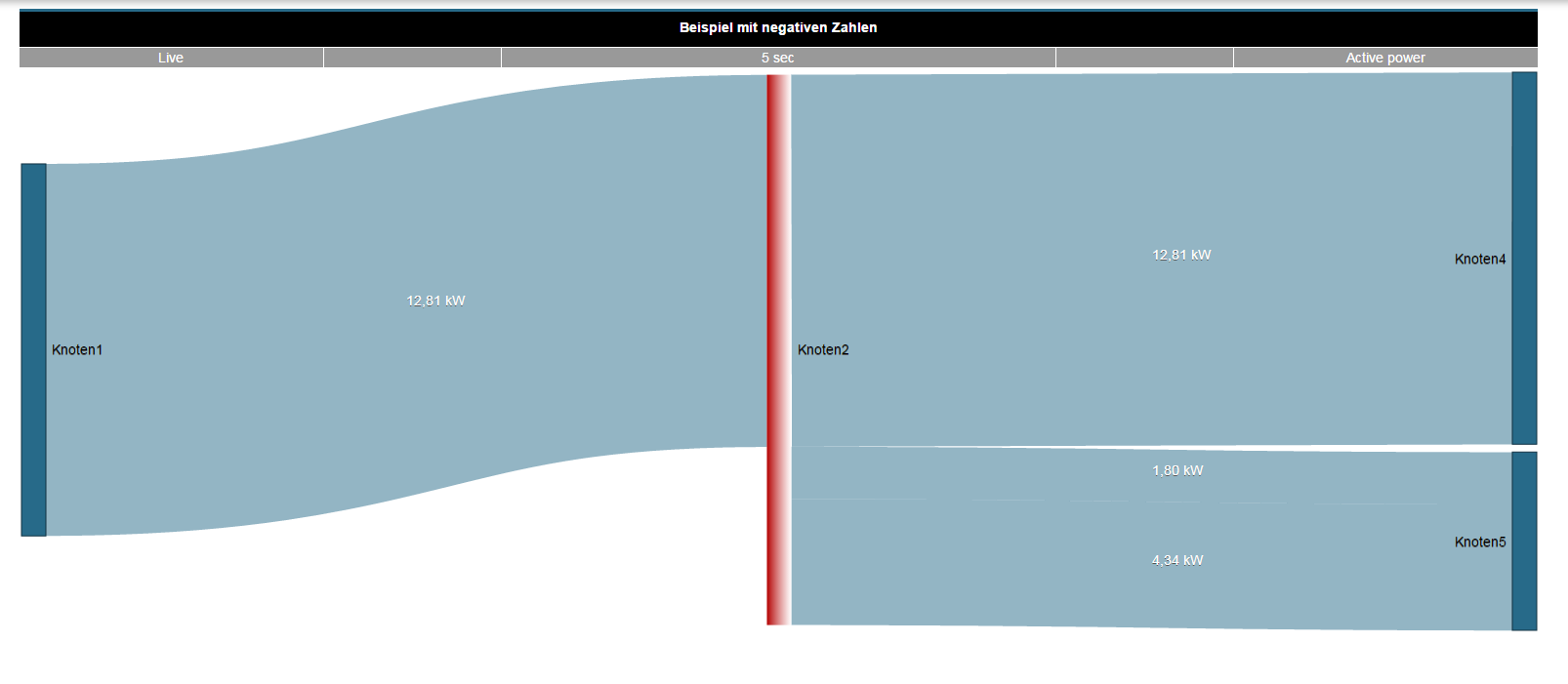
Ejemplo de un diagrama Sankey:
| Anker |
|---|
| allgemeinebeschreibung_sankey |
|---|
| allgemeinebeschreibung_sankey |
|---|
|
Descripción general:
Diagrama Sankey
- Los flujos de energía (flujos de cantidad) se muestran gráficamente mediante diagramas.
- Las áreas de conexión muestran datos de consumo u otros valores de medición de manera proporcional a la magnitud del valor de medición.
- Puede crearse fácil e intuitivamente con el configurador de Sankey y administrarse con el administrador de Sankey.
- Puede integrarse como widget en cualquier panel y evaluarse.
La función Sankey se compone de tres paneles:
| 1. | Administrador de Sankey | Herramienta de gestión de diagramas Sankey. |
| 2. | Configurador de Sankey | Creación de diagramas Sankey personalizados. |
3. | Widget de Sankey | Puede colocarse en el panel. |
| Anker |
|---|
| sankeymanager |
|---|
| sankeymanager |
|---|
|
Administrador de Sankey
El administrador de Sankey es la herramienta de gestión de diagramas Sankey.
El administrador de Sankey se encarga de las siguientes tareas:
- Administra todos los diagramas Sankey.
- Proporciona una vista general estructurada e informativa de todos los diagramas Sankey existentes.
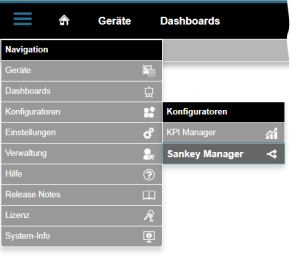
¿Cómo abro el administrador de Sankey?
- Haga clic en el botón «Navegación
 » de la barra de navegación.
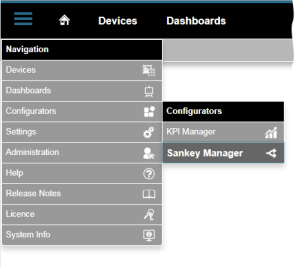
» de la barra de navegación. - Puede acceder al «Administrador de Sankey
 » desde el menú desplegable en «Configuradores
» desde el menú desplegable en «Configuradores  ».
».
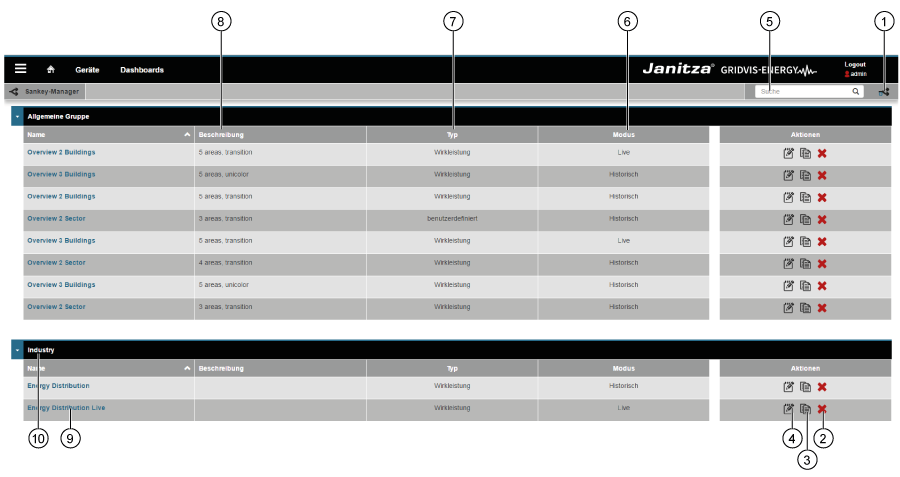
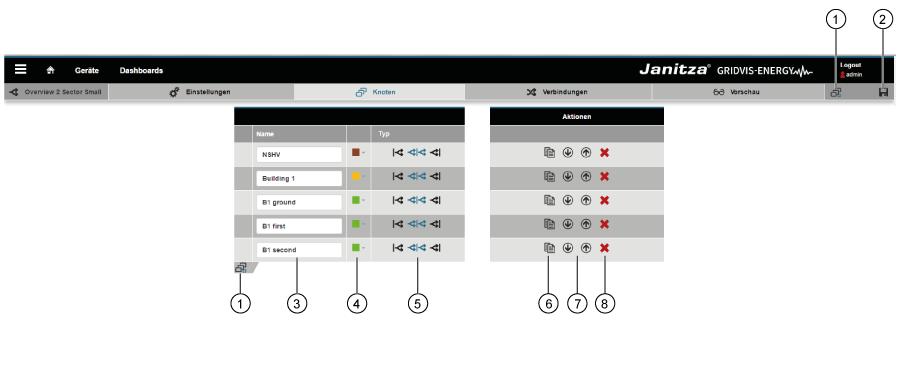
Panel «Administrador de Sankey» (ventana de vista general):
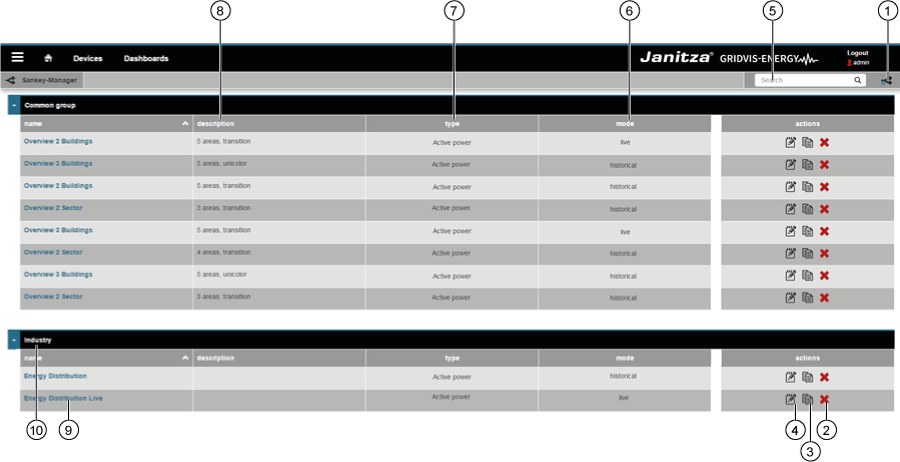
| Pos. | Icono | Texto breve | Descripción |
|---|
| 1 |  | crear | Creación de un nuevo diagrama Sankey. |
| 2 |  | eliminar | Eliminación de un diagrama Sankey. |
| 3 |  | copiar | Copiado de un diagrama Sankey. |
| 4 |  | abrir | Apertura del configurador de Sankey. |
| 5 |  | buscar y filtrar | Búsqueda y filtrado de un diagrama Sankey. |
| 6 |
| Modo | Modo del diagrama Sankey. El diagrama Sankey muestra «valoresen tiempo real» o ««valoresdel historial». |
| 7 |
| Tipo | Tipo del valor de medición (p. ej., potencia activa). |
| 8 |
| Descripción | Texto informativo sobre un diagrama Sankey guardado anteriormente. |
| 9 |
| Nombre | Nombre del diagrama Sankey. Haciendo clic en el nombre se abre una vista previa. |
| 10 |
| Grupo | Grupo del diagrama Sankey. Puede configurarse en el configurador de Sankey. |
| Anker |
|---|
| sankeykonfigurator |
|---|
| sankeykonfigurator |
|---|
|
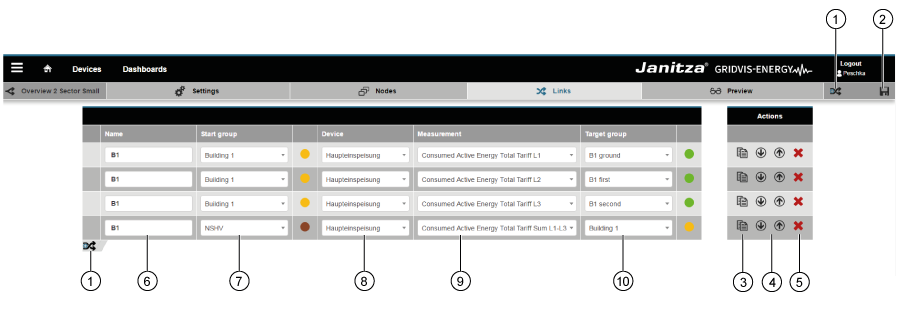
Configurador de Sankey
Con el configurador de Sankey puede crear sus propios diagramas Sankey aunque no tenga conocimientos de programación. Para dibujar un diagrama Sankey, utilice el configurador de Sankey para crear nodos y conexiones, y vincularlos unos con otros en función de sus necesidades (véase también la descripción «Nodos y conexiones»).
El configurador de Sankey se caracteriza por los siguientes aspectos:
- Está compuesto por cuatro paneles (ajustes, nodos, conexiones y vista previa).
- Sirve para ajustar diagramas Sankey personalizados —sin requerir conocimientos de programación— mediante la creación y vinculación de nodos y conexiones.
- Sirve, por ejemplo, para crear análisis del flujo de la energía de su empresa sin gran esfuerzo. También puede seleccionar y visualizar valores de medición, como la corriente, la potencia activa o las oscilaciones superiores. El requisito para realizar análisis del flujo de la energía consiste en emplear dispositivos de medición de, por ejemplo, la empresa Janitza. Estos deben colocarse en los puntos de medición deseados y vincularse por medio del configurador de Sankey.
- Se abre para cada diagrama Sankey haciendo clic en el botón «
 » del panel de «acciones» del administrador de Sankey.
» del panel de «acciones» del administrador de Sankey.
(véase la pantalla «Administrador de Sankey» en la pos. 4).
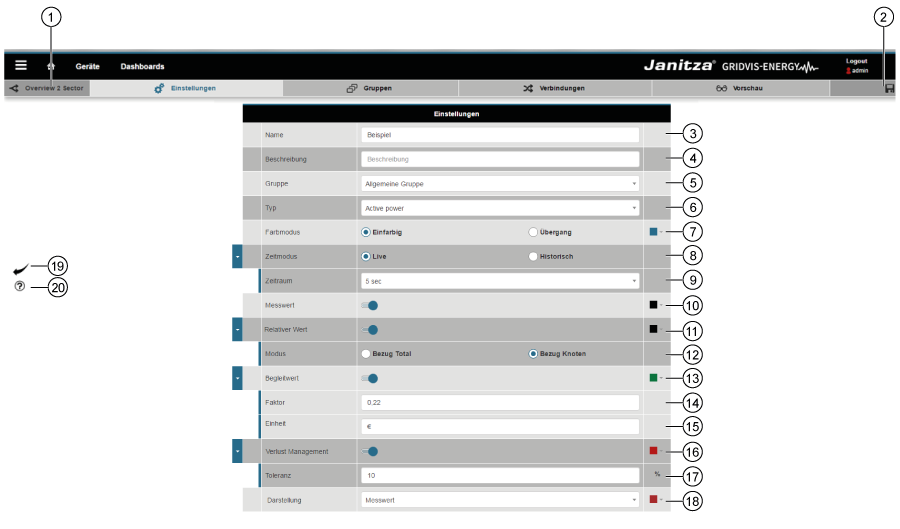
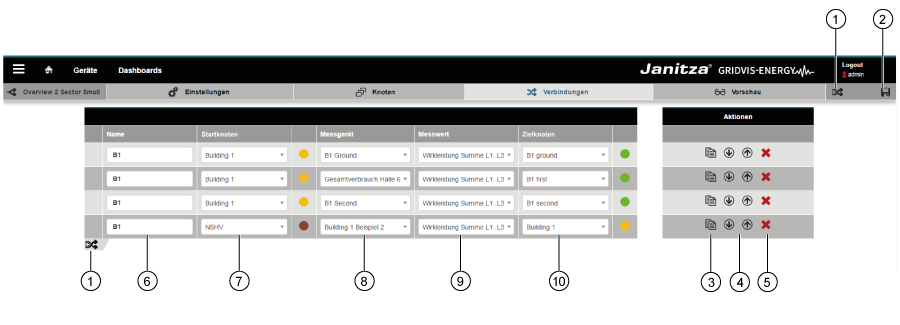
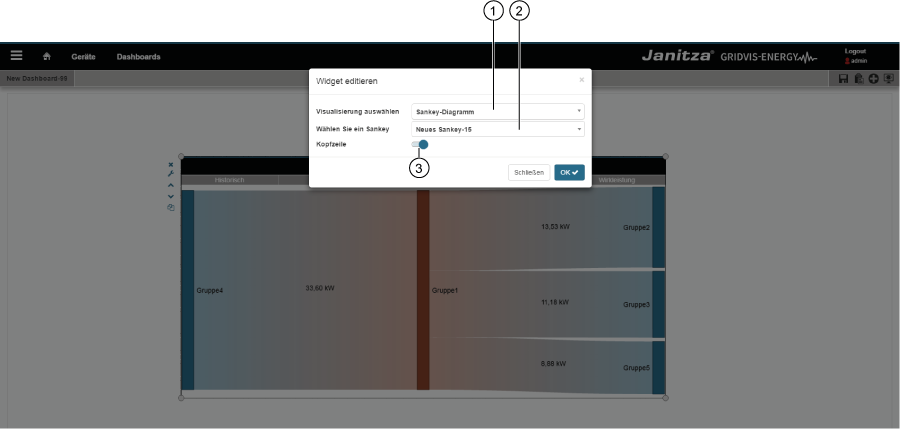
Ajustes
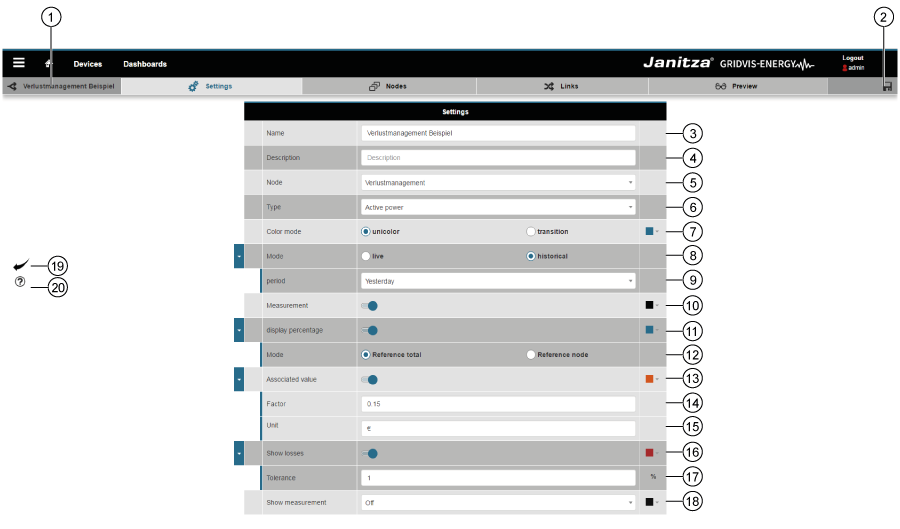
| Pos. | Icono | Texto breve | Descripción |
|---|
| 1 |  | Nombre del diagrama Sankey. |
|
| 2 |  | Guardar | - Se guardan los ajustes realizados.
- Se accede automáticamente al siguiente panel (pestaña).
|
| 3 |
| Nombre | - Nombre del diagrama Sankey.
- El diagrama Sankey aparece como widget en el administrador de Sankey y el panel debajo de su nombre.
|
| 4 |
| Descripción | - Información sobre el diagrama Sankey.
- La entrada aparece en el administrador de Sankey.
|
| 5 |
| Grupo | - Introducción de nombres de grupos personalizados a los cuales está asignado el diagrama Sankey (véase el administrador de Sankey en la pos. 10).
- Puede elegir los nombres de grupos ya existentes en un campo de selección de apertura que se abre.
- Los grupos sirven para disponer de una estructura clara en el administrador de Sankey.
- Los grupos nuevos pueden crearse introduciendo datos
|
| 6 |
| Tipo | El requisito para crear un diagrama Sankey consiste en elegir el tipo de valor de medición.
La elección del tipo de valor de medición tiene efecto en el panel «Conexiones» (véase abajo: «Nodos y conexiones»).
Pueden elegirse los siguientes tipos de valores de medición: - Potencia activa
- Potencia aparente
- Corriente
- Energía activa
- Definido por el usuario (elección de todos los tipos de valores de medición).
|
| 7 |
| Modo de color | Selección del modo de color para las conexiones: - Monocromático (color seleccionable)
- Traspaso (gradientes).
Para las conexiones pueden emplearse los colores de los nodos con el botón de selección «Traspaso» activado
(ajustable en el panel «Nodos» del configurador Sankey). |
| 8 |
| Modo de tiempo | Selección de los valores del historial y en tiempo real: - El modo «En tiempo real» muestra los valores actuales
- El modo «Del historial» muestra los valores registrados
|
| 9 |
| Periodo de tiempo | El configurador de Sankey requiere introducir el periodo de tiempo en ambos modos (valores del historial y en tiempo real).
En función del modo, la introducción del periodo de tiempo tiene distintos efectos: - Para el modo «En tiempo real» se selecciona la frecuencia de actualización
- En cuanto al modo «Del historial», tienen lugar las siguientes acciones:
- Los valores de consumo (p. ej., energía activa) se determinan y visualizan a lo largo de un periodo de tiempo.
- Para los valores de medición (p. ej., corriente, potencia) se crea y visualiza un valor medio aritmético de todos los valores de medición.
|
| 10 |
| Valor de medición | Si el control deslizante está activado, tienen lugar las siguientes acciones: - Manteniendo el puntero del ratón sobre una conexión del diagrama Sankey, aparece el valor de medición (véase el punto 6: «Tipo») como «información sobre herramientas».
- Si el ajuste de visualización (punto 18) está establecido como «Valor de medición», este aparece directamente en la conexión del diagrama Sankey.
- Puede configurar el color del «valor de medición» mediante el cuadro de diálogo.
|
| 11 |
| Valor relativo | Si el control deslizante está activado, tienen lugar las siguientes acciones: - Manteniendo el puntero del ratón sobre una conexión del diagrama Sankey, aparece el valor de medición «valor relativo» en porcentaje («información sobre herramientas»).
- Si el ajuste de visualización (punto 18) está establecido como «Valor relativo», la magnitud relativa aparece directamente en la conexión del diagrama Sankey.
- Puede configurar el color del «valor relativo» mediante el cuadro de diálogo.
|
| 12 |
| Modo | Botón de selección «Consumo total» activado: - La magnitud relativa del valor de medición se corresponde con todos los valores de medición.
Botón de selección «Nodos de consumo» activado: - La magnitud del valor de medición se corresponde con los nodos individuales .
|
| 13 |
| Valor asociado | El valor asociado muestra el valor de medición multiplicado por un factor y provisto de una unidad; así, por ejemplo, pueden visualizarse de un vistazo «costes» (o magnitudes similares) en las conexiones de su diagrama Sankey. Si el control deslizante está activado, tienen lugar las siguientes acciones: - Manteniendo el puntero del ratón sobre una conexión del diagrama Sankey, aparece el valor de medición —provisto de un factor y una unidad— como «valor asociado» (información sobre herramientas»).
- Si el ajuste de visualización (punto 18) está establecido como «valor asociado», este aparece directamente en la conexión del diagrama Sankey.
- Puede configurar el color del «valor asociado» mediante el cuadro de diálogo.
|
| 14 |
| Factor | Campo de entrada «Factor»: El factor es el operando que se multiplica por su valor de medición y da como resultado el valor asociado en función de la unidad (punto 15) de que disponga. |
| 15 |
| Unidad | Campo de entrada «Unidad»: Unidad del valor asociado. |
| 16 |
| Gestión de pérdidas | Si el control deslizante está activado, tienen lugar las siguientes acciones: - El sistema calcula la pérdida que se produce entre la entrada y la salida de un nodo.
- Las desviaciones se visualizan como pérdida en el diagrama Sankey introduciendo una tolerancia. Parpadean los nodos que presenten pérdidas.
- Puede configurar el color para las «pérdidas» mediante el cuadro de diálogo.
|
| 17 |
| Tolerancia | Campo de entrada «Tolerancia»: - Valor expresado en porcentaje con el cual se activa la gestión de pérdidas (los nodos parpadean).
|
| 18 |
| Visualización | La lista de selección «Visualización» cuentan con cuatro ajustes: - Apagado
- Valor de medición
- Valor relativo
- Valor asociado
El ajuste seleccionado aparece directamente en la conexión del diagrama Sankey (véase el ejemplo de «indicador de información sobre herramientas», mostrado más abajo). |
| 19 |  | Botón «Atrás» | Haciendo clic en el botón se vuelve al administrador de Sankey |
| 20 |  | Botón «Ayuda» | - Ayuda directa (parte inferior izquierda de la ventana).
- Con el botón se accede a esta página de ayuda. Usted volverá a estar en la página anterior después de cerrar la página de ayuda.
|
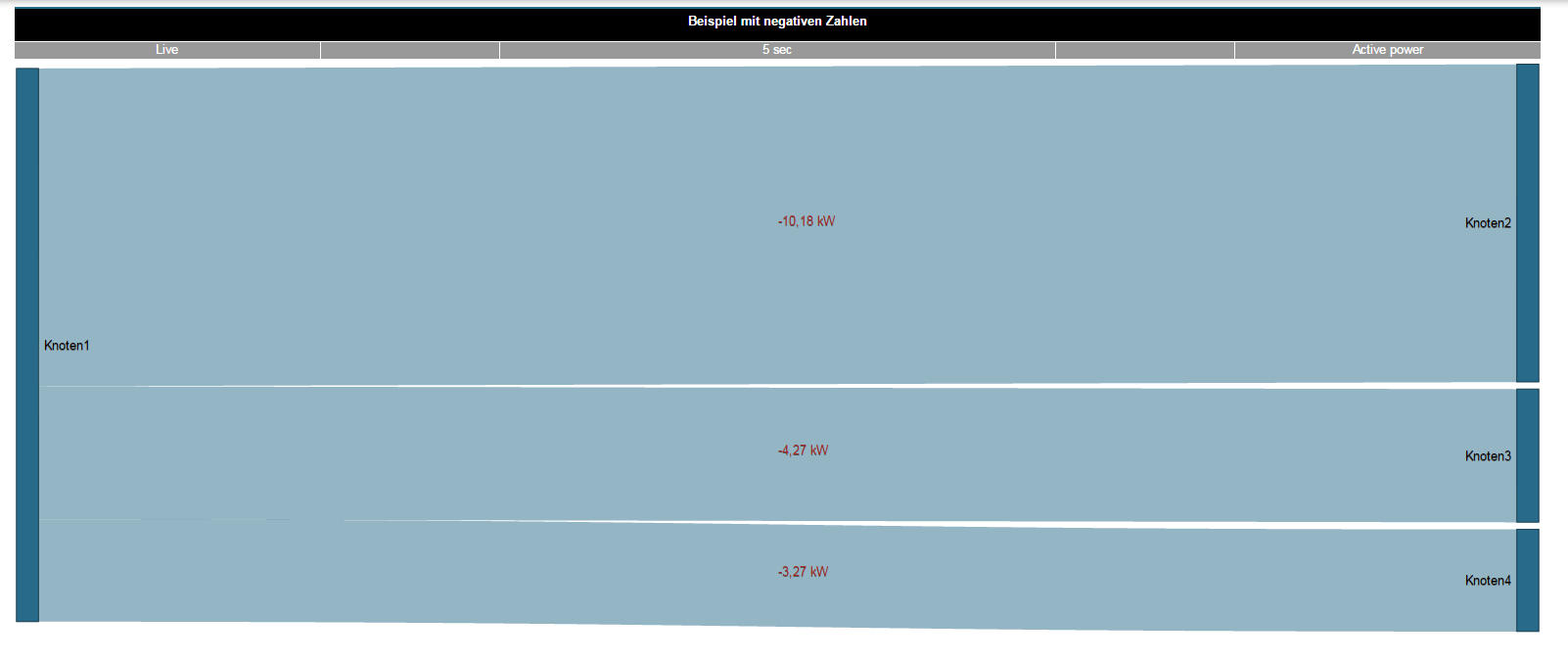
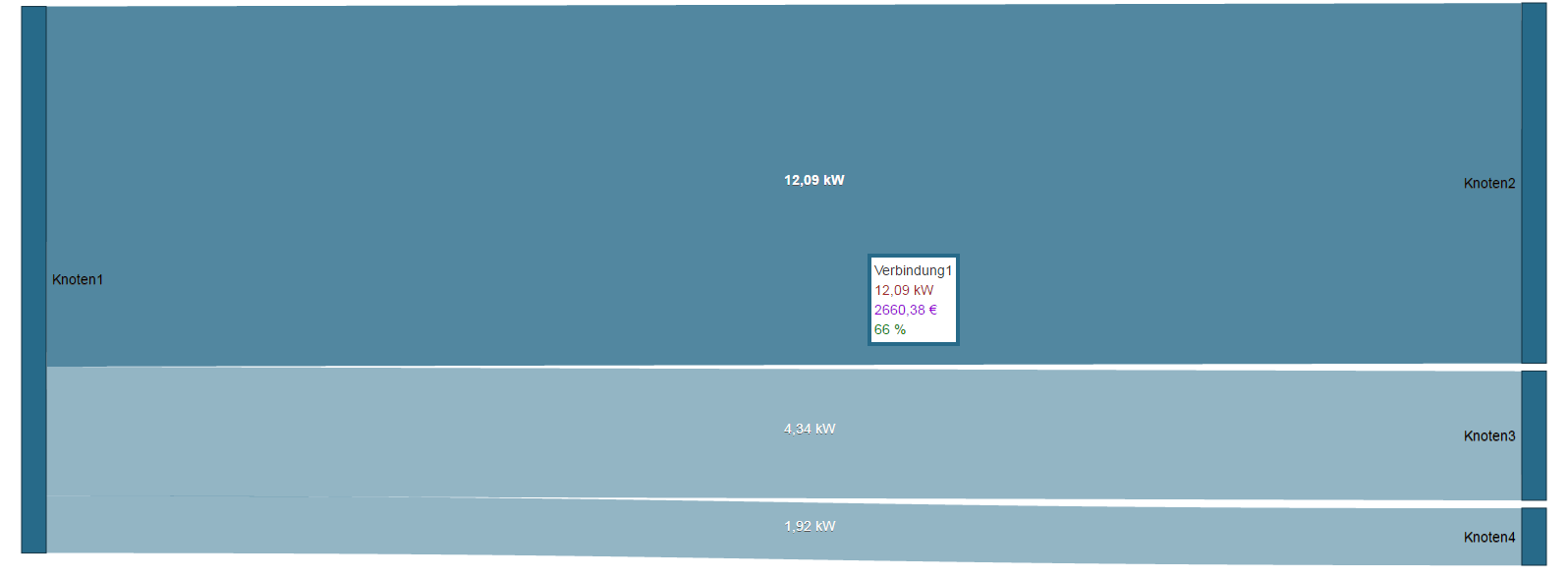
Ejemplo de «indicador de información sobre herramientas»:

Para este ejemplo están activados los siguientes controles deslizantes:
- Valor de medición (en kW)
- Valor relativo (en porcentaje)
- Valor asociado (en euros)
El ajuste de la lista de selección «Visualización» es «Valor de medición».
| Info |
|---|
|
En la instalación de GridVis Desktop pueden configurarse dispositivos virtuales (VD) . Con losdispositivos virtualespueden sumarse distintos valores de medición. El resultado correspondiente puede seleccionarse como dispositivo independiente. Esta aplicación es muy útil para sustituir un valor de medición que falte. |
| Anker |
|---|
| gruppen_u_verbind |
|---|
| gruppen_u_verbind |
|---|
|
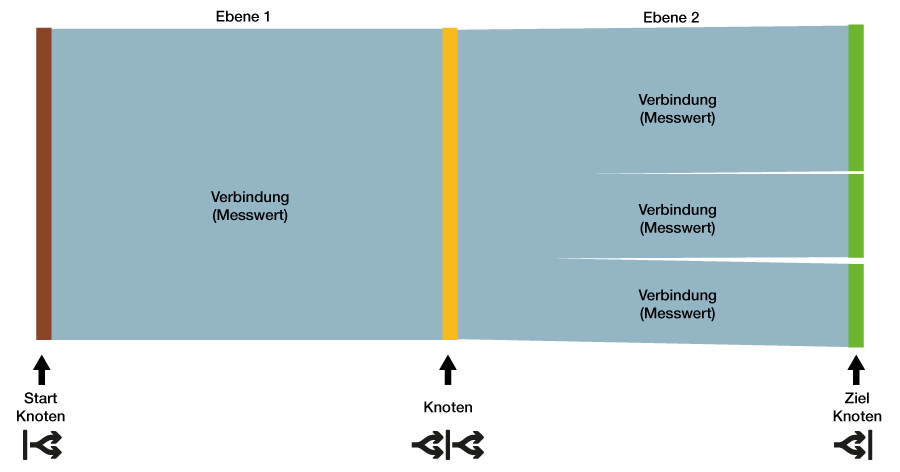
Nodos y conexiones: explicación
- Unaconexión es un área entre dos nodos
- Una conexión representa un valor de medición como área.
- Unnodo no es un valor de medición.
- Los nodos son agrupamientos o una unión de conexiones (valores de medición).
- Los nodos pueden presentar varias conexiones o únicamente una conexión.
- Los nodosposeen conexiones de entrada y salida.
- Los nodos iniciales poseen exclusivamente conexiones de salida.
- Los nodos de destino poseen exclusivamente conexiones de entrada.

| Panel | Función | Descripción |
|---|
| Nodos | - Nodos intermedios
- Nodos iniciales y de destino
| En el configurador de Sankey pueden definirse los nodos creados como nodos iniciales, intermedios o de destino. Los nodos poseen colores y nombres propios. |
| Conexiones | - Área(s) entre nodos
- Valor de medición
| El área de una conexión muestra la relación de aspecto (del valor de medición) en relación con el plano en su conjunto. Se emplea una conexión para conectar dos nodos entre sí. |
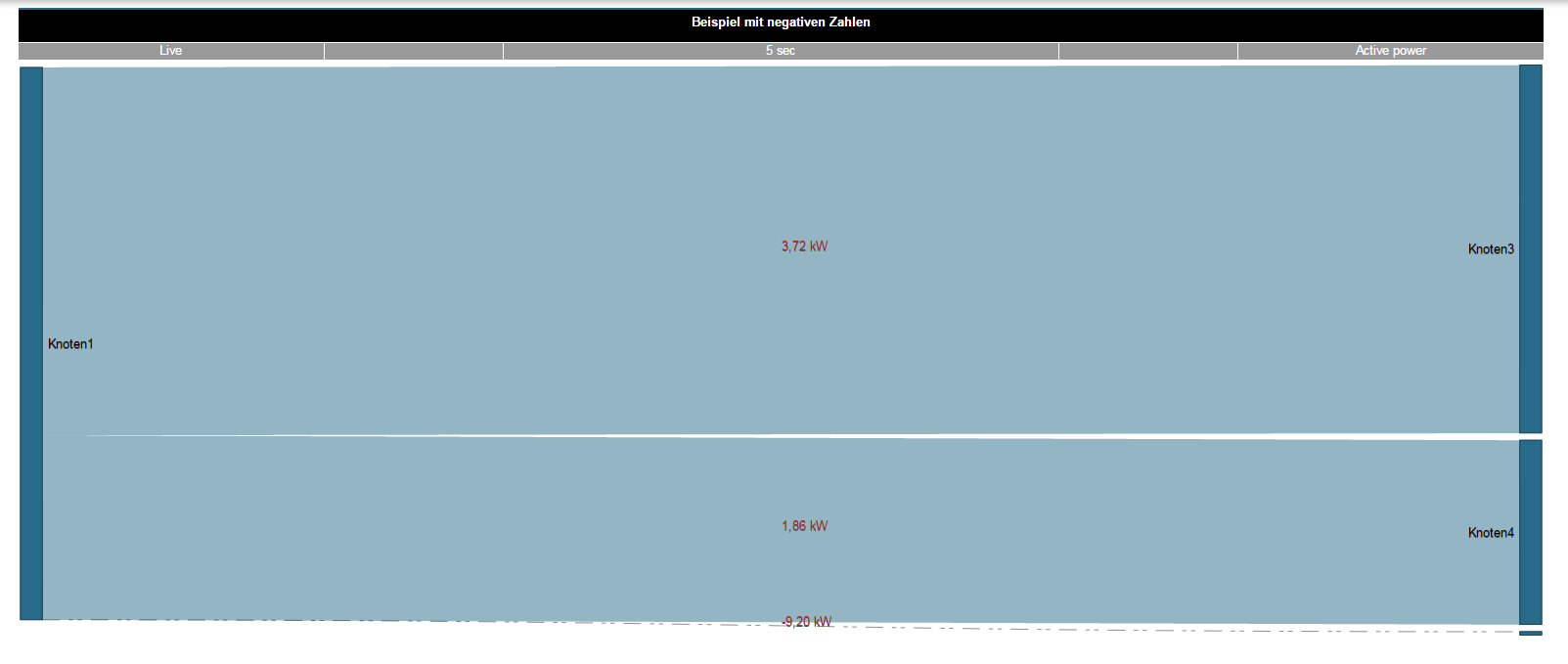
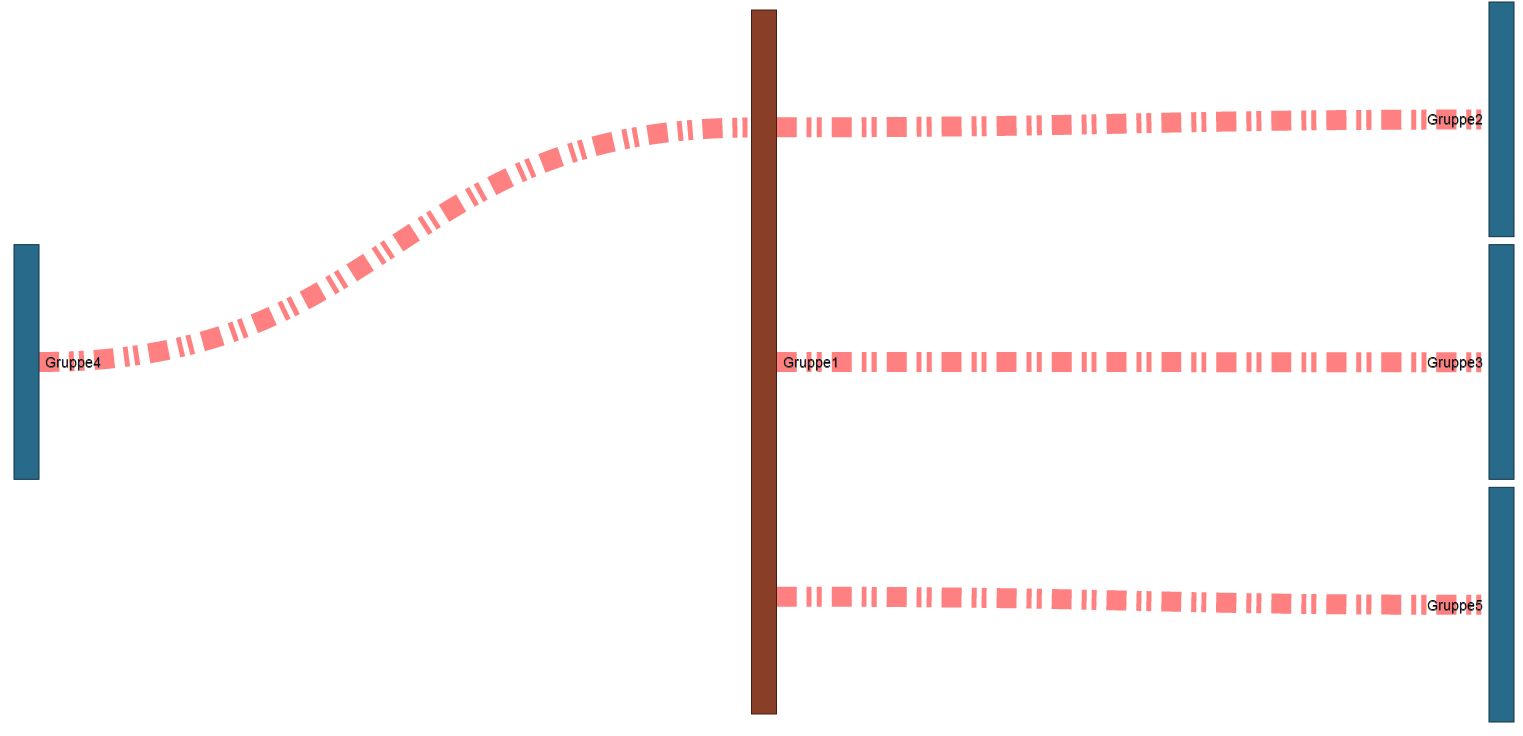
 Nota:
Nota:
Si faltan valores de medición para crear un diagrama Sankey (p. ej., los valores de medición se encuentran en el futuro o faltan registros),
el sistema representa los valores de medición (conexiones) para el diagrama Sankey por medio de líneas rojas discontinuas:
| Info |
|---|
|
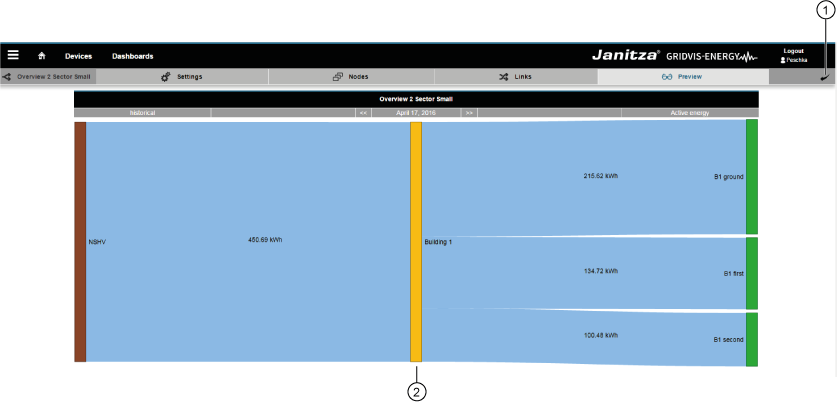
¡Para crear diagramas Sankey complejos, resulta importante y útil conectar los distintos nodos, así como visualizar y verificar el resultado con la «función de vista previa»! |