| Sv translation | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Sv translation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
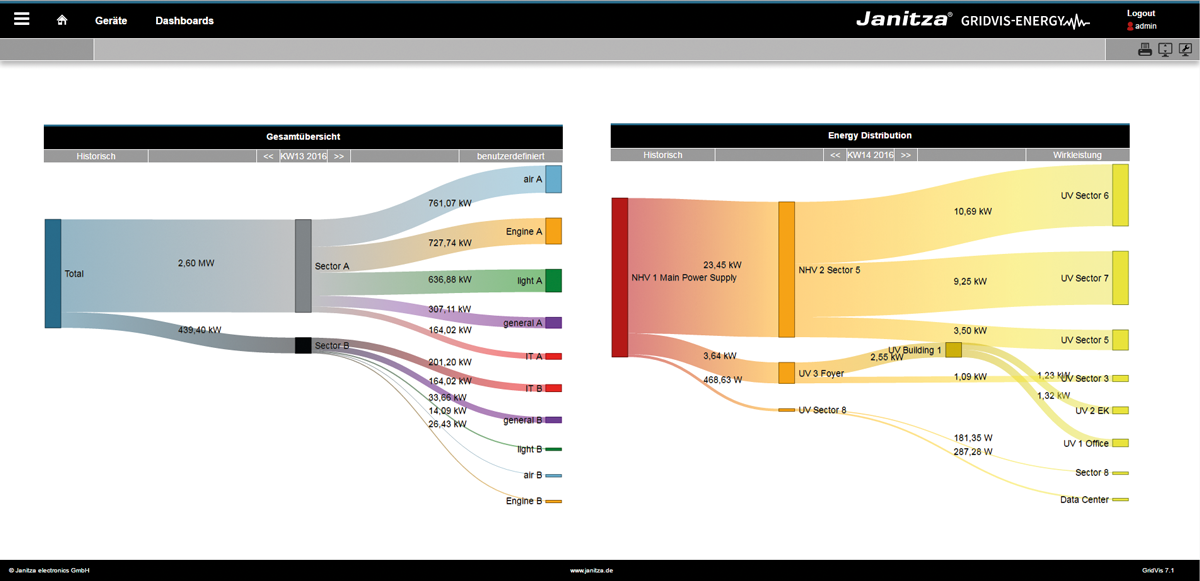
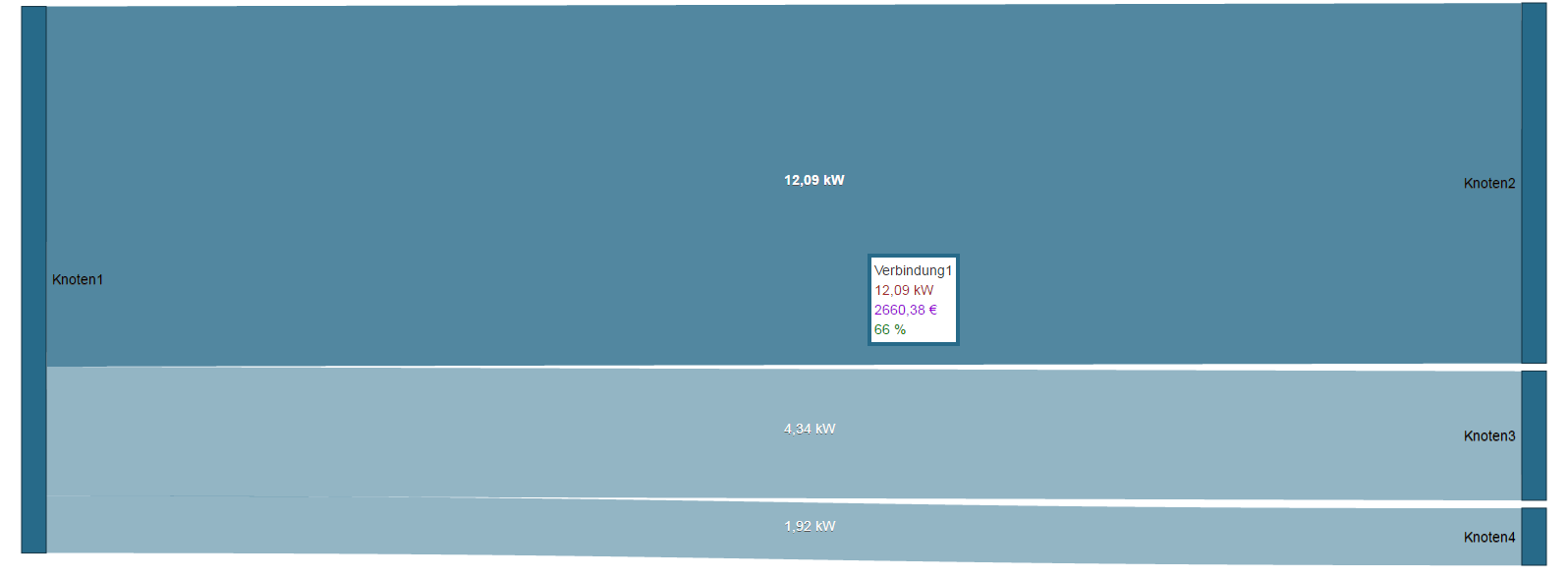
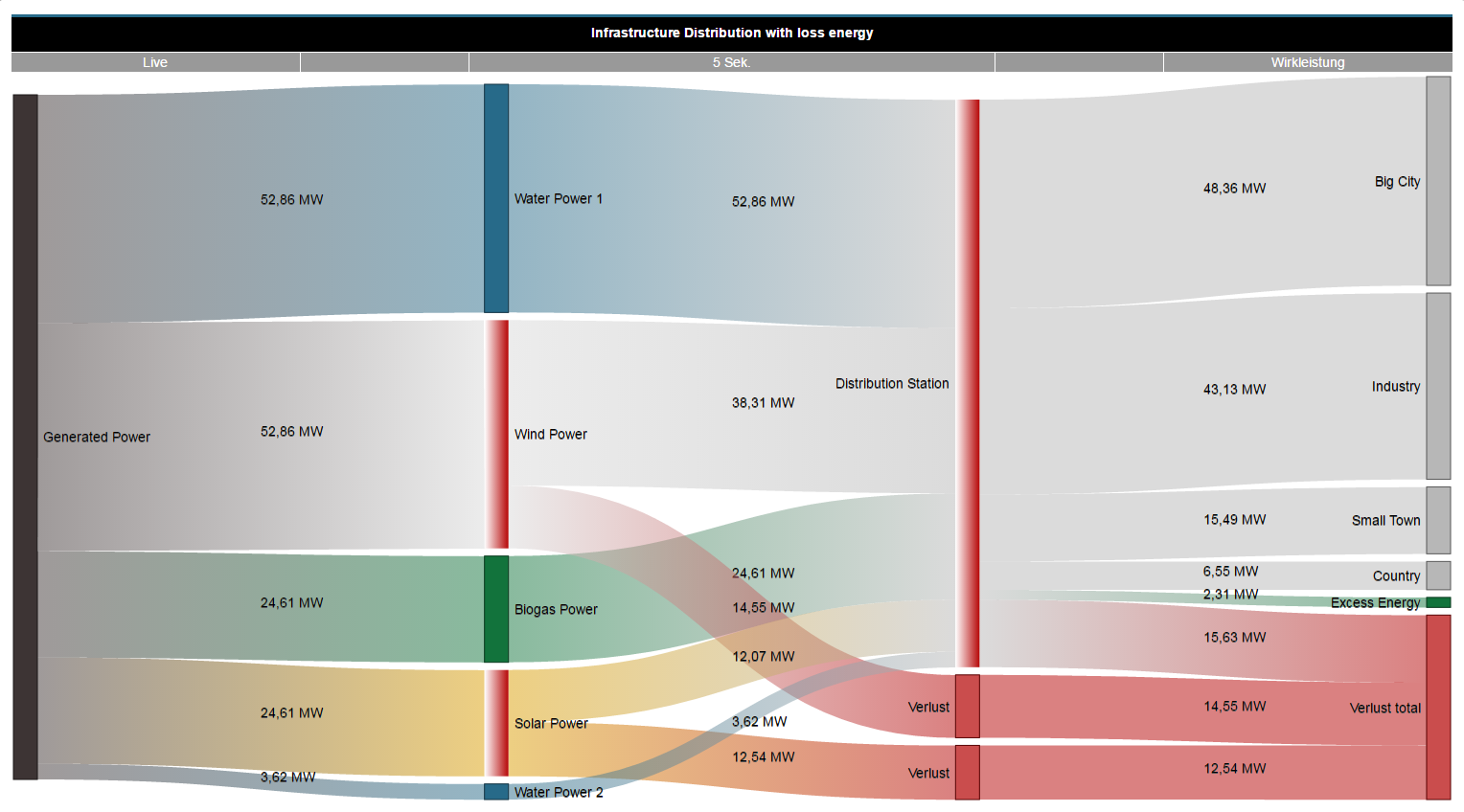
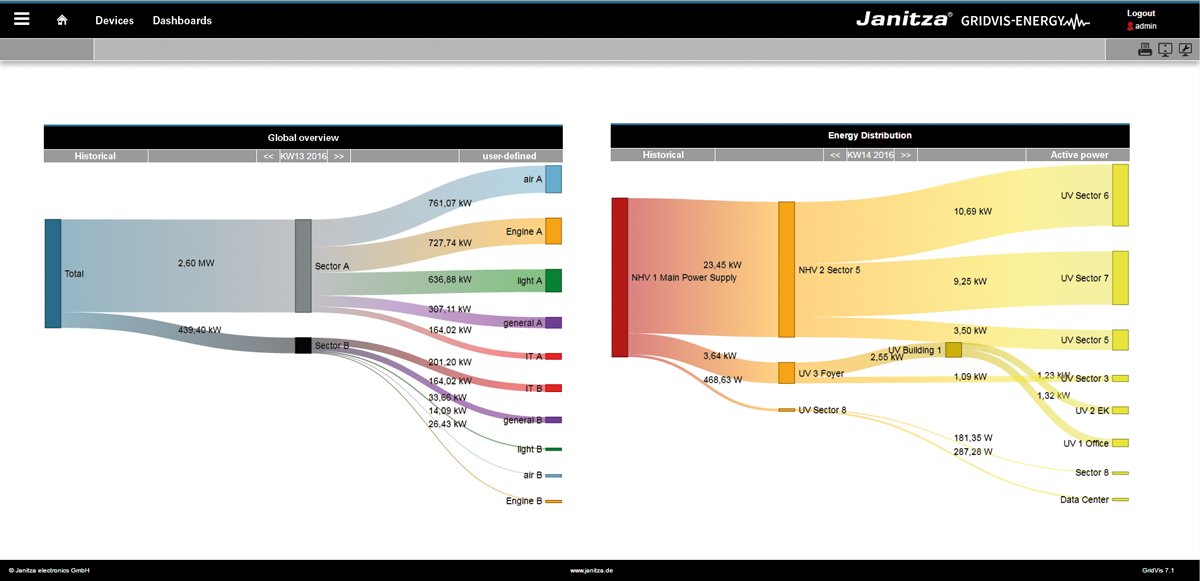
Sankey diagramWithin the framework of the energy flow analyses, relevant energy consumption values are required. In order to analyse these, they are arranged in informative energy flow diagrams (Sankey diagrams). With a Sankey diagram, you obtain a transparent and clear graphic illustration of your energy consumption and other measured values. With the Sankey function, comprising the 3 areas of Sankey Manager, Sankey Configurator and Sankey Widget, you generate your own Sankey diagrams tailored to your company - easily, intuitively and without any programming knowledge - which can be integrated in every dashboard as a widget, for the purpose of energy flow analysis and evaluation. Example of a Sankey diagram:
The Sankey diagram
The Sankey function consists of 3 areas:
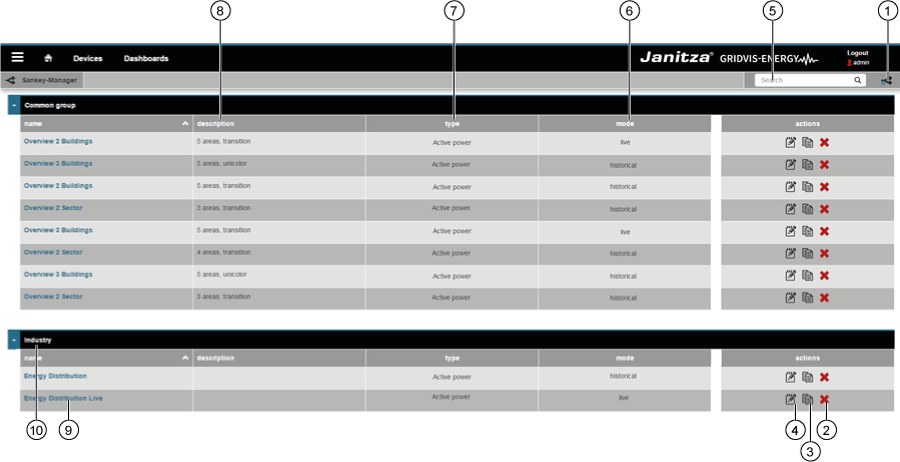
The Sankey Manager is the management tool for Sankey diagrams. The Sankey Manager
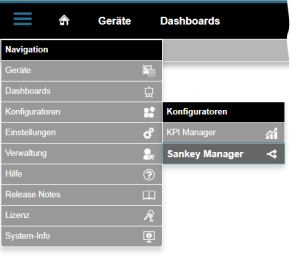
How do I open the Sankey Manager?
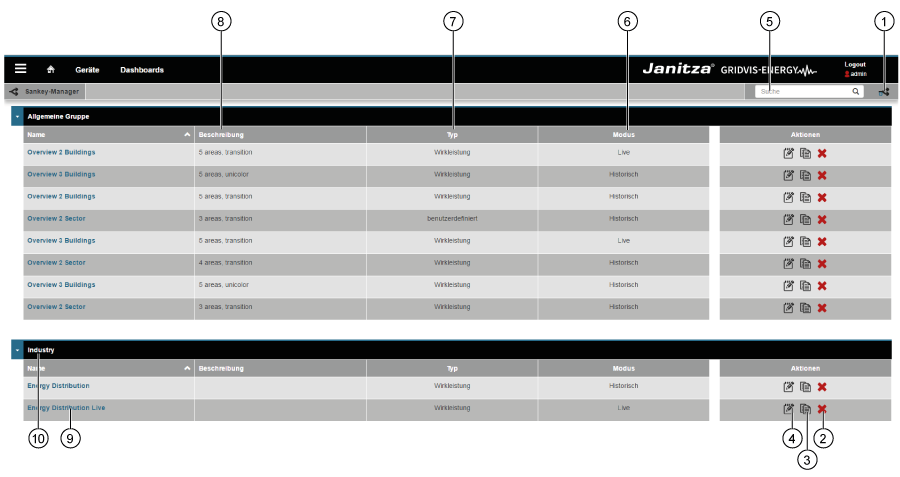
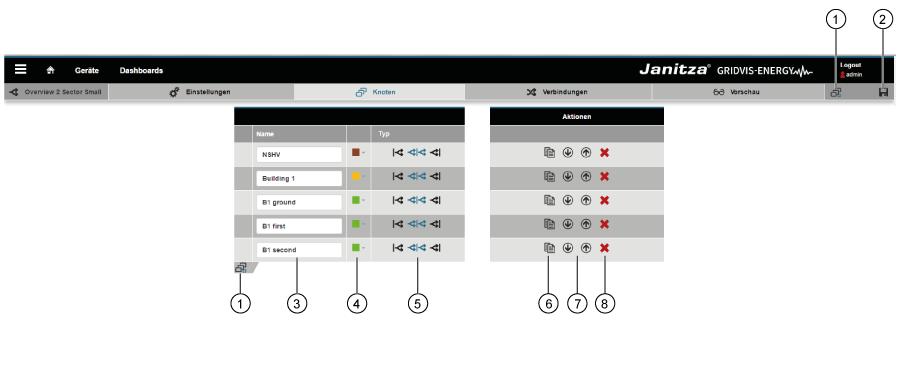
"Sankey Manager" area (overview window):
Using the Sankey Configurator, you create your own Sankey diagrams without programming knowledge. In order to create a Sankey diagram, you create nodes and connections in the Sankey Configurator and link these with each other, according to requirement (see also description of "Nodes and links"). The Sankey Configurator
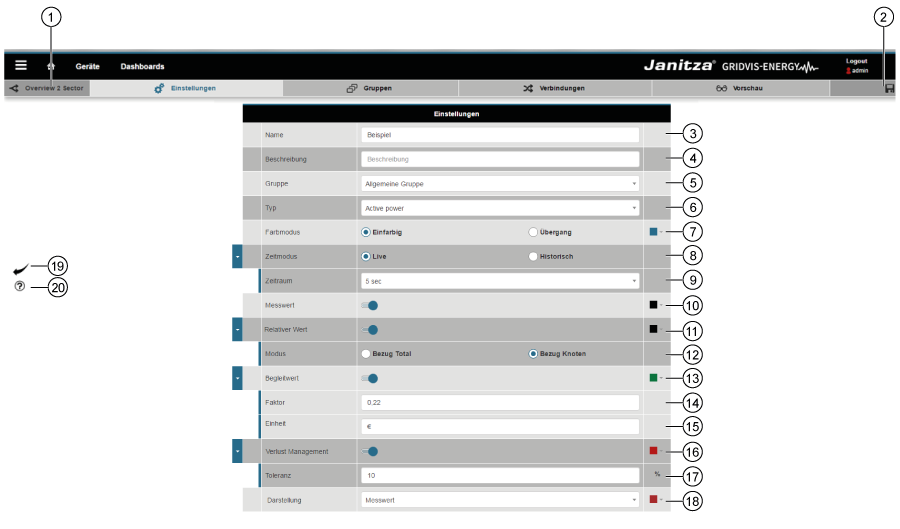
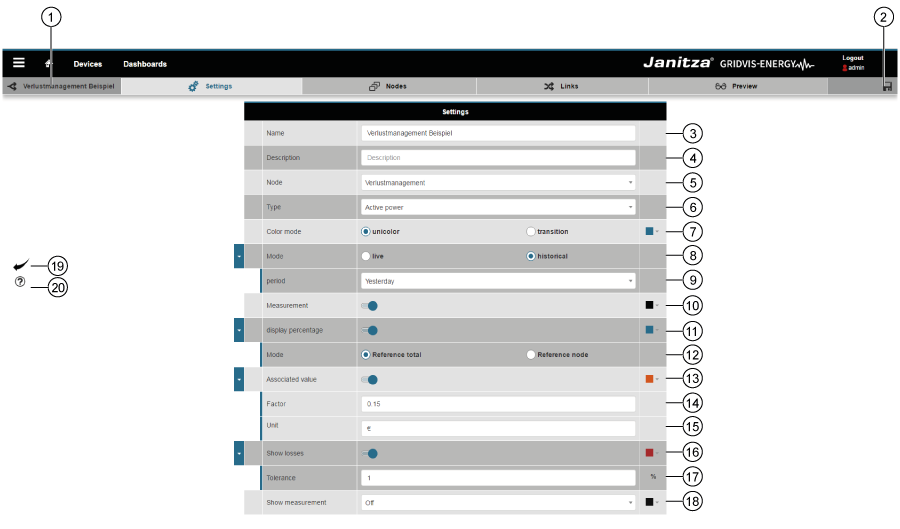
Settings
Example of “tool tip display”: In this example, the following slide controls are activated:
The setting in the “Show measurement” selection list is “Measured value”.
Note: If measured values required for the creation of a Sankey diagram are missing (e.g. measured values lie in the future or recordings are missing),
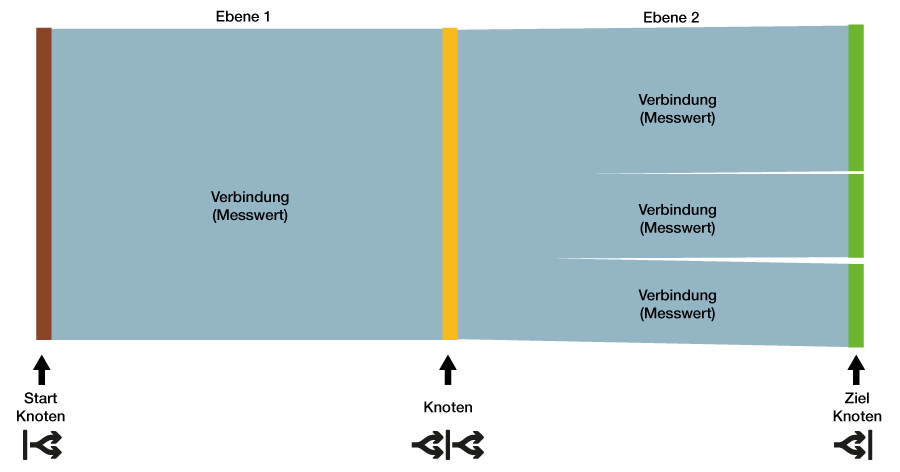
Nodes A node
The system marks unused nodes. In the “Links” window (sub-navigation > "Links" tab), you link unused nodes and the system removes the marking.
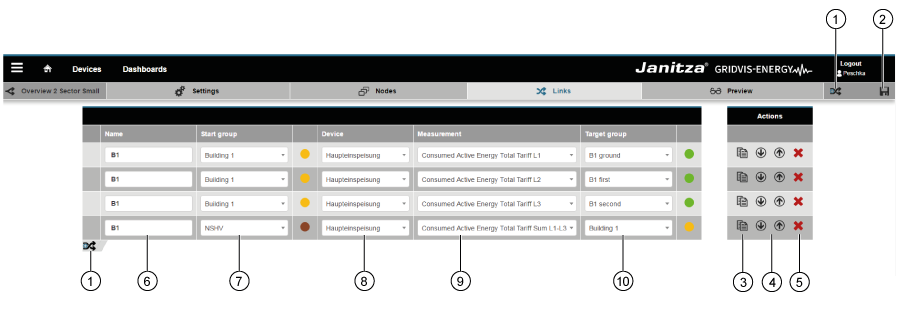
Links
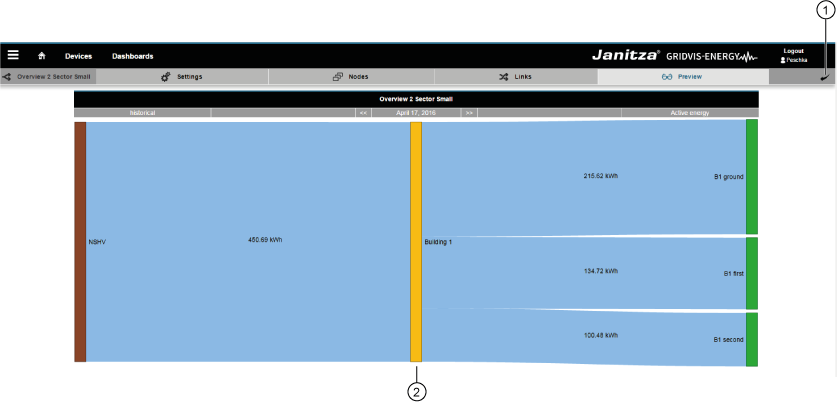
Clicking on the “Preview” button in the sub-navigation provides you with a preview of your Sankey diagram.
Sankey diagramWithin the framework of the energy flow analyses, relevant energy consumption values are required. In order to analyse these, they are arranged in informative energy flow diagrams (Sankey diagrams). With a Sankey diagram, you obtain a transparent and clear graphic illustration of your energy consumption and other measured values. With the Sankey function, comprising the 3 areas of Sankey Manager, Sankey Configurator and Sankey Widget, you generate your own Sankey diagrams tailored to your company - easily, intuitively and without any programming knowledge - which can be integrated in every dashboard as a widget, for the purpose of energy flow analysis and evaluation. Example of a Sankey diagram: Anker | allgemeinebeschreibung_sankey | allgemeinebeschreibung_sankey | General description:The Sankey diagram
The Sankey function consists of 3 areas:
Anker | sankeymanager | sankeymanager | The Sankey ManagerThe Sankey Manager is the management tool for Sankey diagrams. The Sankey Manager
How do I open the Sankey Manager?
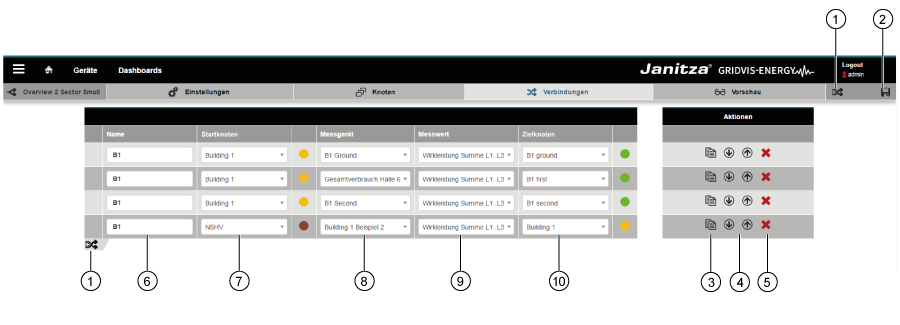
"Sankey Manager" area (overview window): Item Icon Short text Description 1 | Create Create new Sankey diagram. 2 | Delete Delete Sankey diagram. 3 | Copy Copy Sankey diagram. 4 | Open Open Sankey Configurator. 5 | Search and filter Search and filter Sankey diagrams. 6 | Mode Sankey diagram mode. The Sankey diagram shows "live values" or "historical values". 7 | Type Type of measured value (e.g. effective power). 8 | Description Information text that has been stored with a Sankey diagram. 9 | Name Name of the Sankey diagram. Clicking on the name opens a preview. 10 | Group Sankey diagram group. Can be configured in the Sankey Configurator.
Anker | sankeykonfigurator | sankeykonfigurator | The Sankey ConfiguratorUsing the Sankey Configurator, you create your own Sankey diagrams without programming knowledge. In order to create a Sankey diagram, you create nodes and connections in the Sankey Configurator and link these with each other, according to requirement (see also description of "Nodes and links"). The Sankey Configurator
Settings Item | Icon | Short text | Description | 1 | Name of the Sankey diagram. 2 | Save
3 | Name
4 | Description
5 | Group
6 | Type A precondition for the creation of a Sankey diagram is the selection of the measured value type.
7 | Colour mode Selection of the colour mode for the links:
(Can be set in the “Nodes” area of the Sankey Configurator). 8 | Time mode Choose between live or historical values:
9 | Time period The Sankey Configurator requires entry of the period in both modes (live and historical values).
10 | Measured value With activated slide control:
11 | Relative value With activated slide control:
12 | Mode Activated radio button - “Reference total”:
Activated radio button - “Reference node”:
13 | Associated value The associated value shows the measured value, multiplied by a factor and assigned a unit. In this way it is possible to visualise e.g. the “costs” (or similar) in your Sankey diagram links at a glance. With activated slide control:
14 | Factor “Factor” input field:
15 | Unit “Unit” input field:
16 | Loss management With activated slide control:
17 | Tolerance “Tolerance” input field:
18 | Show measurement The “Show measurement” selection list has 4 settings:
19 | “Back” button Clicking on the button takes you back to the Sankey Manager 20 | “Help” button
Example of “tool tip display”: In this example, the following slide controls are activated:
The setting in the “Show measurement” selection list is “Measured value”.
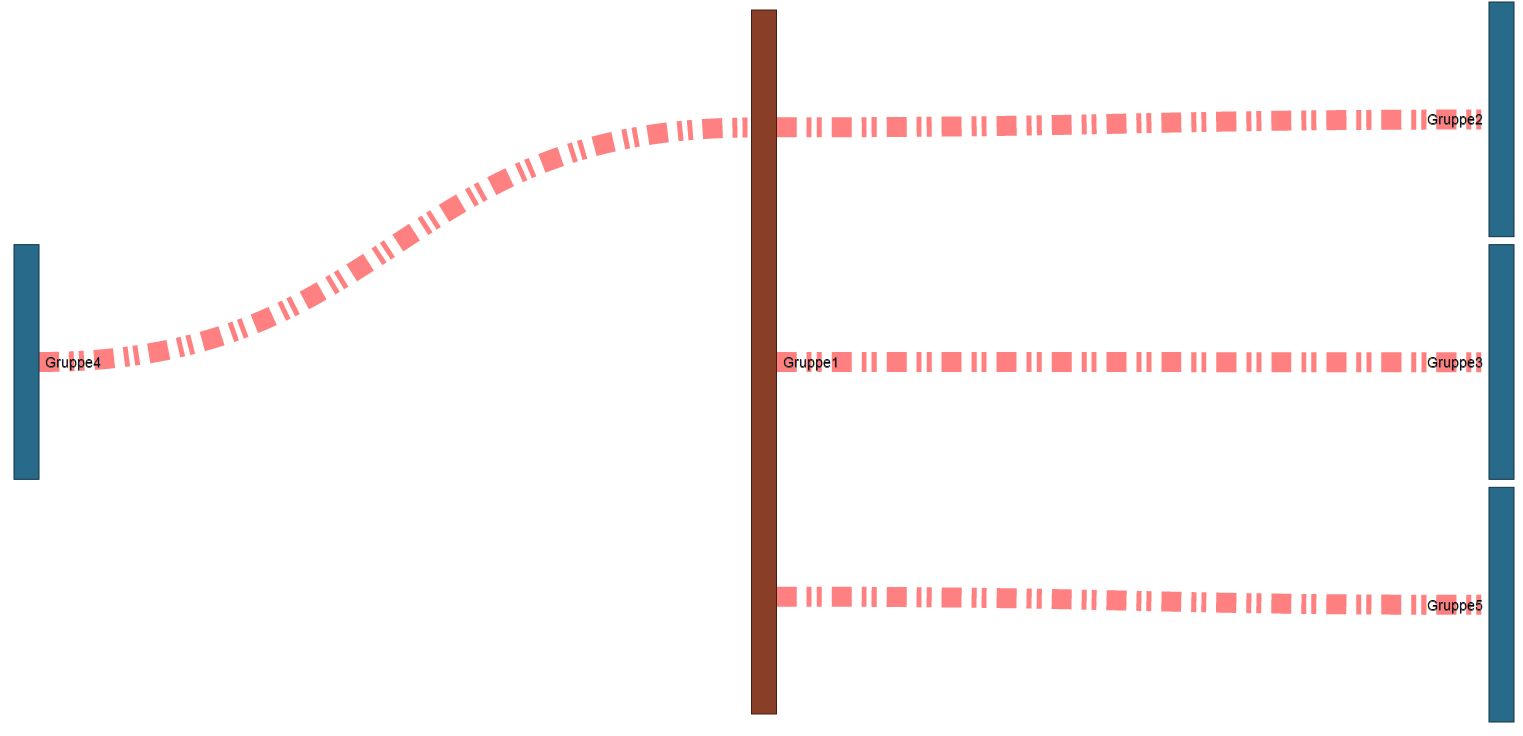
Anker | gruppen_u_verbind | gruppen_u_verbind | Nodes and links - explanation
Note: If measured values required for the creation of a Sankey diagram are missing (e.g. measured values lie in the future or recordings are missing),
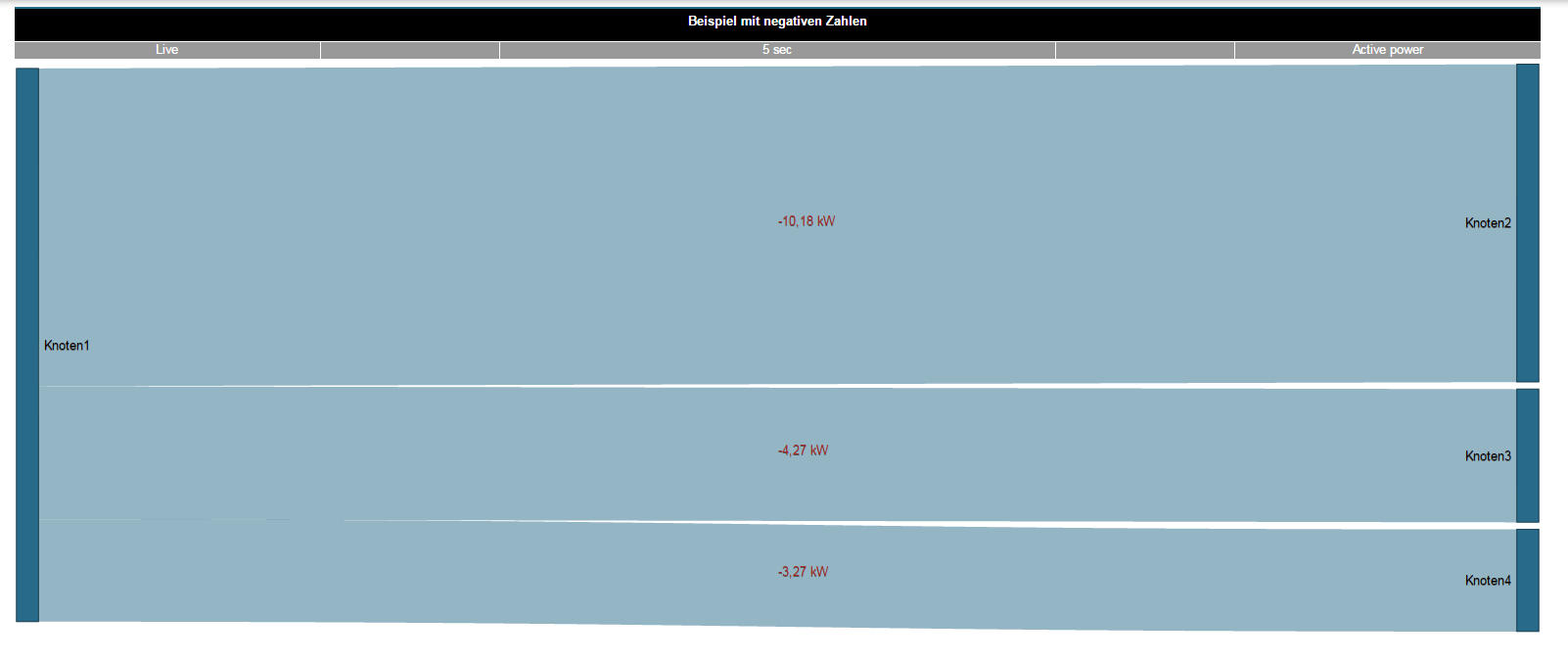
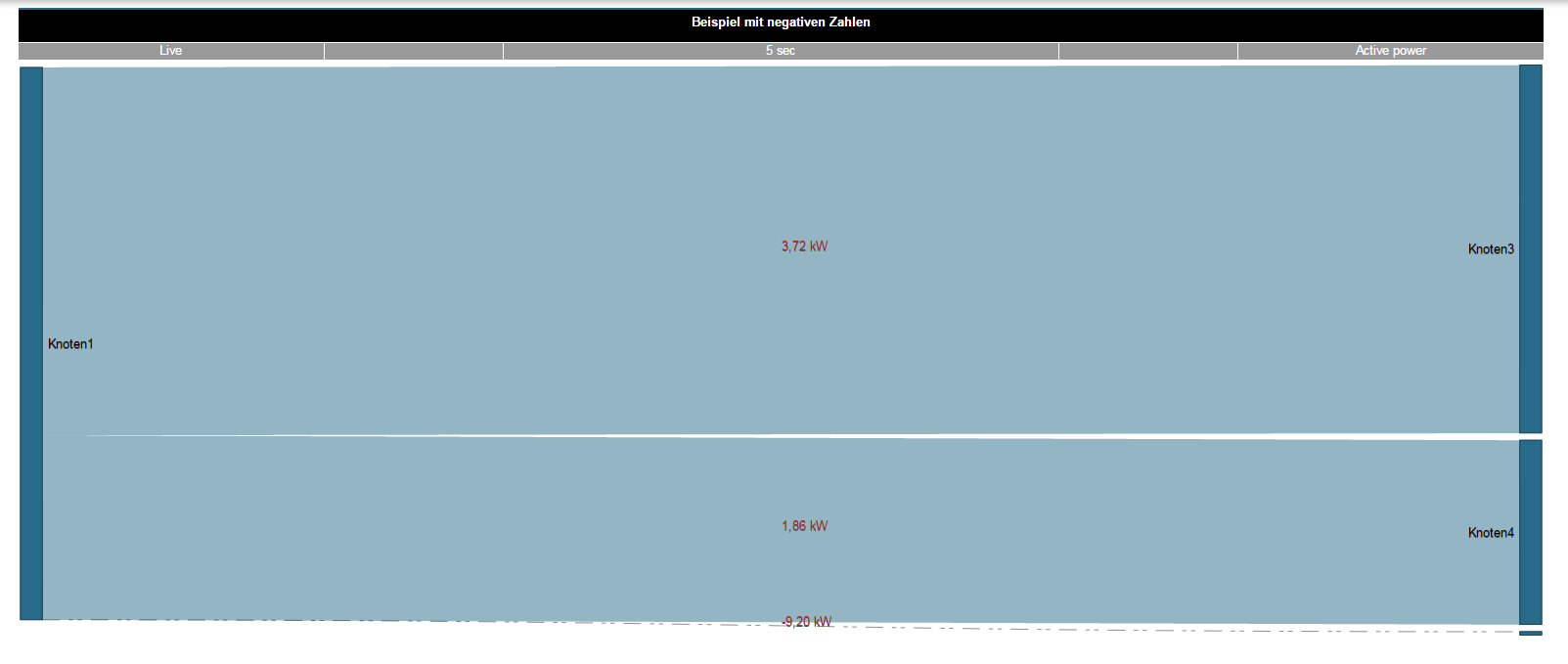
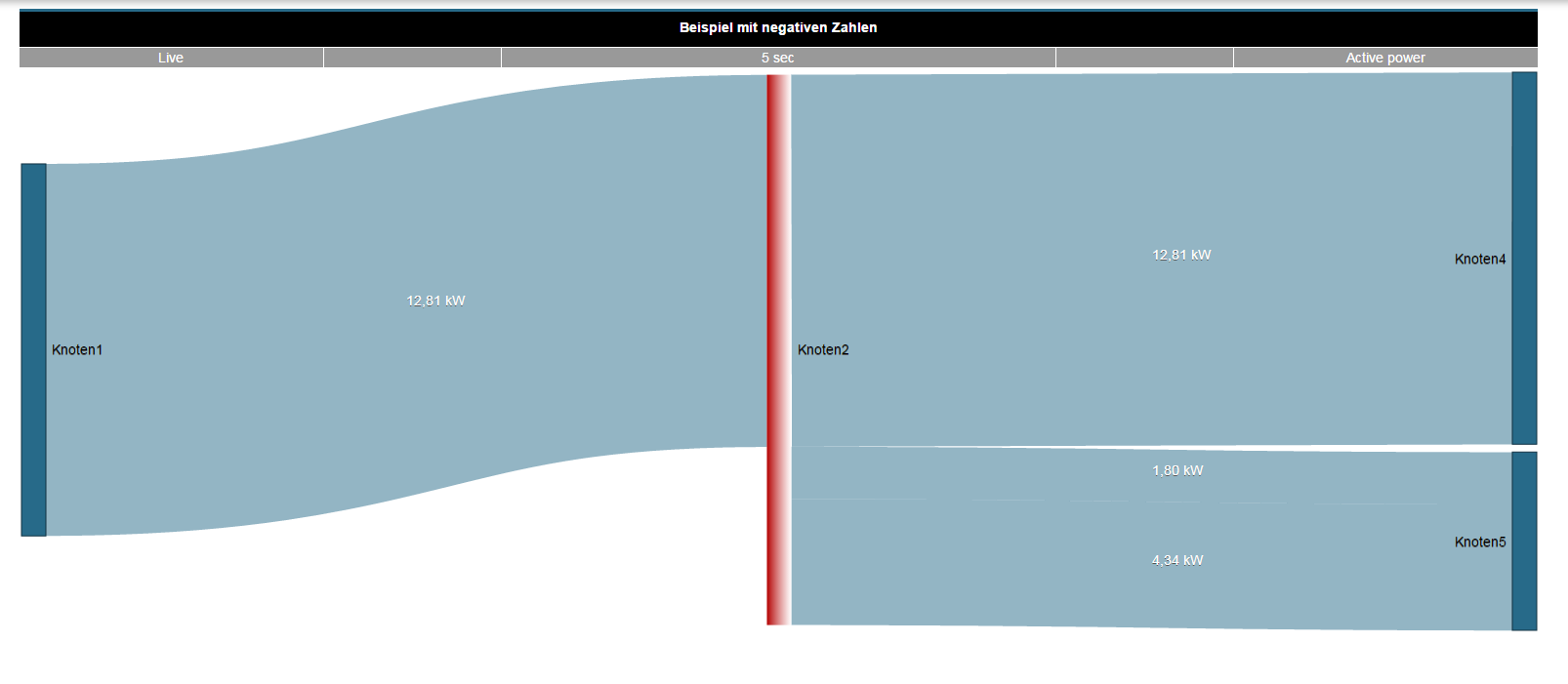
Example 1: Positive and negative measured values in a Sankey diagram. Example 2: Sankey diagram with exclusively negative measured values.
Once created, Sankey diagrams can be placed on existing or new dashboards as widgets.
Nodes A node
The system marks unused nodes. In the “Links” window (sub-navigation > "Links" tab), you link unused nodes and the system removes the marking.
Links
Item | Icon | Short text | Description | 1 | Insert link | Insert new link. 2 | Save link Save configuration settings of the link. 3 | Copy link | Clicking on the button copies the selected link. 4 | Position of the link | Shift created links up or down in the configuration window. Note: This function
5 | Delete link | Note: Deleted links cannot be restored! 6 | Name of the link | Appears in the Sankey diagram as a tool tip, if the mouse is moved over the link. 7 | Start node | Shows the node types start and intermediate node. Note:
8 | Measuring devices selection | Note: |
Note:
9 | Measured value selection | Note:
10 | Target node | Shows the node types target and intermediate node. Note:
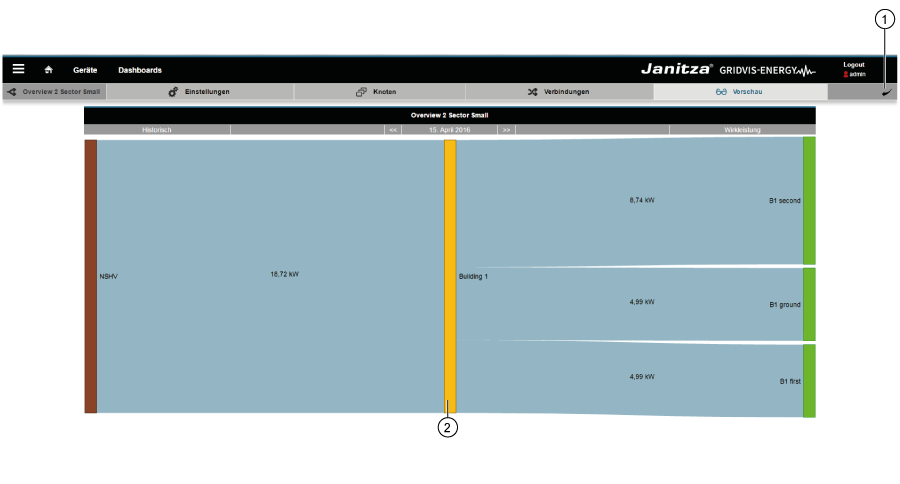
Anker | vorschau | vorschau | The preview functionClicking on the “Preview” button in the sub-navigation provides you with a preview of your Sankey diagram. Item | Icon | Short text | Description | 1 | Back Go back to the Sankey Manager 2 | Preview Preview of the Sankey diagram. Note: If measured values required for the creation of a Sankey diagram are missing (e.g. measured values lie in the future or recordings are missing),
Example 1: Positive and negative measured values in a Sankey diagram. Example 2: Sankey diagram with exclusively negative measured values. Anker | widget | widget | The Sankey WidgetOnce created, Sankey diagrams can be placed on existing or new dashboards as widgets.
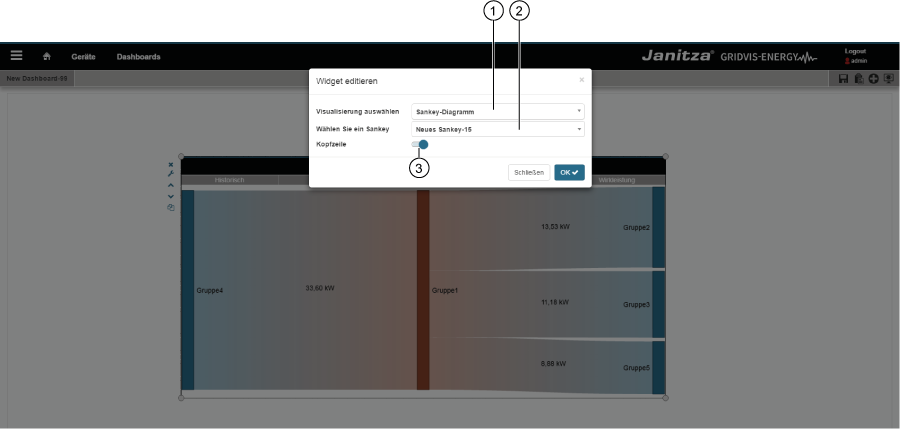
Item | Icon | Short text | Description | 1 | Select visualisation Visualisation selection list: Select "Sankey diagram" widget! 2 | Choose a Sankey Selection list with all Sankey diagrams 3 | Header Slide control for showing or hiding the header. Loss management The system calculates the loss between the input and output of a node. Inputting a tolerance (relative in %) influences the loss. Deviations from the measured values, which exceed the entered tolerance, are plotted on the Sankey diagram as losses (the affected nodes pulsate):
Example 1 “Loss at the node output”
Example 2 “Loss at the node input”
Loss management The system calculates the loss between the input and output of a node. Inputting a tolerance (relative in %) influences the loss. Deviations from the measured values, which exceed the entered tolerance, are plotted on the Sankey diagram as losses (the affected nodes pulsate):
Example 1 “Loss at the node output”
Example 2 “Loss at the node input” |
| Sv translation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||
| Sv translation | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Anker | oben | oben | Anker | oben | oben | Válido paraEdiciones GridVis | Plataforma software | |
| Sv translation | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| Sv translation | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Anker | oben | oben | Anker | inizio | inizio | Valido perEdizioni GridVis | Piattaforma software | |