| Sv translation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
Einstellungen:
Ethernet*
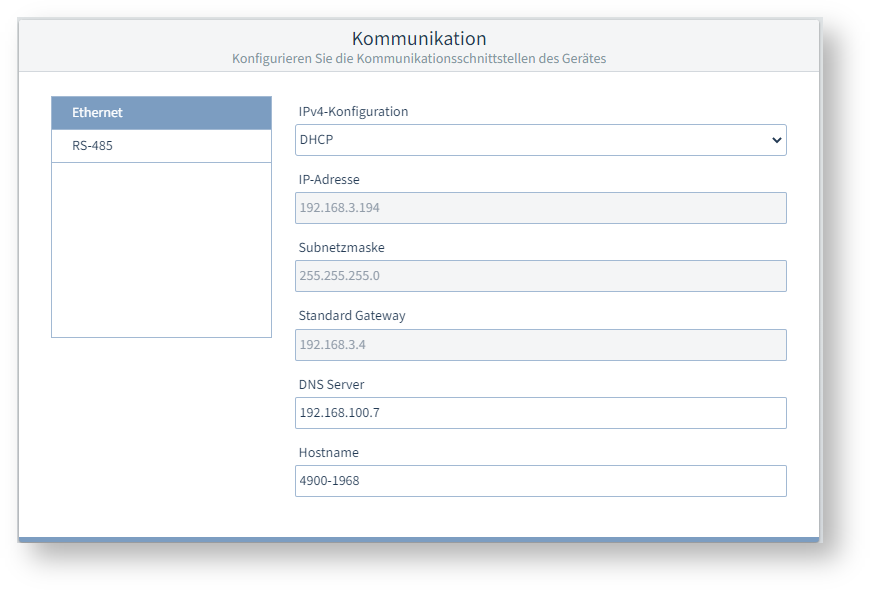
IPv4-KonfigurationSie können zwischen verschiedenen Arten der Adressvergabe im Netzwerk wählen:
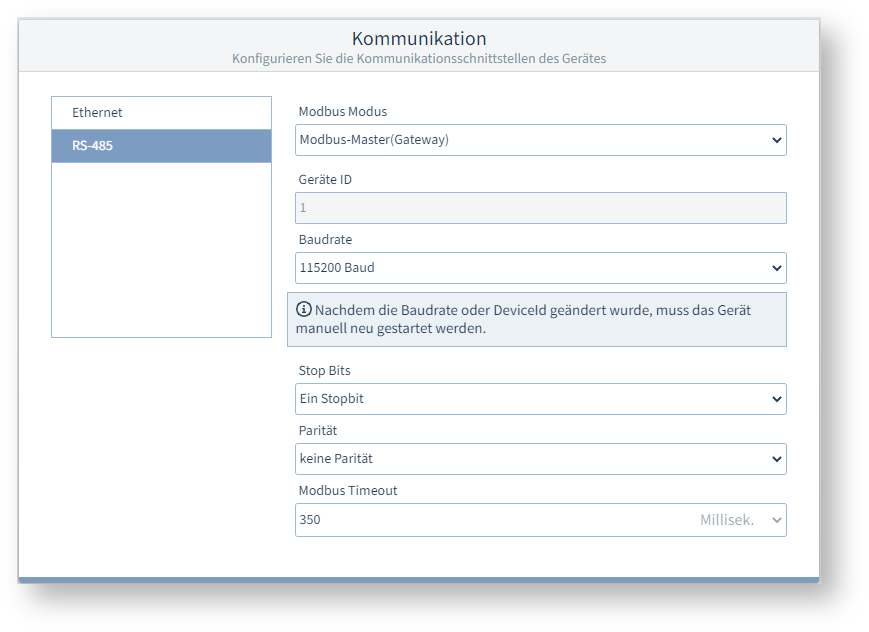
Falls Sie sich für eine feste IP-Adresse entscheiden, müssen Sie die nachfolgenden Einstellungen konfigurieren : IP-Adresse, Subnetzmaske und Standard Gateway. Beispiel-Bild: UMG 96-PA-MID+ DNS ServerDies ist die IP-Adresse des Domain Name Server (DNS), ein System das für die Verknüpfung von Domain-Namen mit IP-Adressen verwendet wird. HostnameDer Hostname ist der Name des Messgeräts zur Kommunikation innerhalb des Netzwerks. RS-485Über die RS-485-Schnittstelle kann das Messgerät über das Protokoll "Modbus RTU" kommunizieren. Modbus Modus
Geräte IDWeisen Sie dem Gerät eine Geräteadresse zu, mit der das Gerät in der Busstruktur angesprochen wird. Jede Geräteadresse existiert in einer Busstruktur nur einmal! BaudrateWählen Sie für alle Geräte in der Busstruktur eine einheitliche Baudrate! Stop Bits, ParitätWählen Sie für alle Geräte in der Busstruktur einen einheitlichen Datenrahmen. Modbus TimeoutWenn ein Modbus-Gerät nicht innerhalb der festgelegten Zeit auf eine Anfrage antwortet, wird dies als Timeout gewertet. Das Gateway antwortet mit einer Modbus Exception. Beispiel-Bild: UMG 96-PA-MID+ |
| Sv translation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
Settings
Ethernet*
IPv4 configurationYou can choose between different types of address assignment in the network:
If you decide to use a fixed IP address, you must configure the following settings: IP address, subnet mask and standard gateway. Example image: UMG 96-PA-MID+ DNS serverThis is the IP address of the Domain Name Server (DNS), which is a system used to associate domain names with IP addresses. HostnameThe hostname is the name of the measurement device for communication within the network. RS-485The measurement device can communicate via the RS-485 interface using the "Modbus RTU" protocol. Modbus mode
Device IDAssign a device address to the device which can be used to address the device in the bus structure. Each device address exists only once in a bus structure! Baud rateSelect a uniform baud rate for all devices in the bus structure! Stop bits, paritySelect a uniform data frame for all devices in the bus structure. Modbus timeoutIf a Modbus device does not respond to a request within the specified time, this is considered a timeout. The gateway responds with a Modbus exception. Example image: UMG 96-PA-MID+ |
| Sv translation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
Ajustes:
Ethernet*
IPv4 Configuration (Configuración IPv4)Usted puede seleccionar diferentes tipos de asignación de la dirección en la red:
Si usted se decide por una dirección IP fija, deberá configurar los siguientes ajustes: IP Address (Dirección IP), Subnet Mask (Máscara de subred) y Standard Gateway (Pasarela estándar). Imagen de ejemplo: UMG 96-PA-MID+ DNS Server (Servidor DNS)Esta es la dirección IP del Domain Name Server (DNS), un sistema que se utiliza para vincular nombres de dominio con direcciones IP. Hostname (Nombre del host)El nombre del host es el nombre del dispositivo de medición para la comunicación dentro de la red. RS485A través de la interfaz RS-485, el dispositivo de medición puede comunicarse por medio del protocolo "Modbus RTU". Modbus mode (Modo Modbus)
Device ID (ID de dispositivo)Asigne una dirección al dispositivo con la que se acceda al mismo en la estructura de bus. ¡Cada dirección de dispositivo existe una sola vez en una estructura de bus! Baud rate (Velocidad en baudios)¡Seleccione una velocidad en baudios uniforme para todos los dispositivos en la estructura de bus! Stop Bits, Parity (Bits de parada, paridad)Seleccione una trama de datos uniforme para todos los dispositivos en la estructura de bus. Modbus timeoutSi un dispositivo Modbus no responde dentro del tiempo establecido a una consulta, esto se evalúa como timeout. La pasarela responderá con una excepción Modbus. Imagen de ejemplo: UMG 96-PA-MID+ |
| Sv translation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
Impostazioni:
Ethernet*
Configurazione IPv4È possibile scegliere tra diversi tipi di allocazione degli indirizzi nella rete:
Se si decide di utilizzare un indirizzo IP fisso, è necessario configurare le seguenti impostazioni: Indirizzo IP, Subnet mask e Gateway standard. Immagine di esempio: UMG 96-PA-MID+ Server DNSÈ l’indirizzo IP del DNS (Domain Name Server), un sistema utilizzato per associare i nomi di dominio agli indirizzi IP. Nome hostIl nome host è il nome dello strumento di misura per la comunicazione all’interno della rete. RS-485Lo strumento di misura può comunicare tramite l’interfaccia RS-485 utilizzando il protocollo "Modbus RTU". Modalità Modbus
ID dispositivoAssegnare un indirizzo al dispositivo con il quale il dispositivo è raggiungibile nella struttura bus. Ogni indirizzo dispositivo è presente una sola volta in una struttura bus! Velocità di trasmissioneSelezionare la stessa velocità di trasmissione per tutti i dispositivi in una struttura bus! Bit di stop, paritàSelezionare lo stesso frame di dati per tutti i dispositivi in una struttura bus. Timeout del ModbusSe un dispositivo Modbus non risponde a una richiesta entro il tempo specificato, questo viene considerato un timeout. Il gateway risponde con un’eccezione Modbus. Immagine di esempio: UMG 96-PA-MID+ |